作者:Li, Y; Kappas, M; Li, YF
影响因子:5.65
刊物名称:JOURNAL OF CLEANER PRODUCTION
出版年份:2018
卷:195 页码:1505-1511
Resilience thinking explores the sustainability discourse and transformation of urban complex systems. From the perspective of urban and human environment, this research simulated the resilience transformation of human-environment systems according to the modified catastrophe theory. The adaptivecycle model was performed an approach to interpret resilience transformations in the interactive human-environment systems. In this study, we quantified the resilience of human and environment subsystems through four models of catastrophe theory (Fold, Cusp, Swallowtail and Butterfly model). The resilience transformation was addressed through the mechanism of adaptive cycle that contained four phases within four different time periods (exploitation-r: 2000-2002; release phase-Ω: 2002-2003; conservation-K: 2004-2008 and exploitation-r: 2008-2010). Ultimately, we explored the key drivers of the transformation in complex human-environmental systems, which included production, energy and pollution. Moreover, understanding the transformations in terms of the human and environmental components were indispensable in urban resilience management.
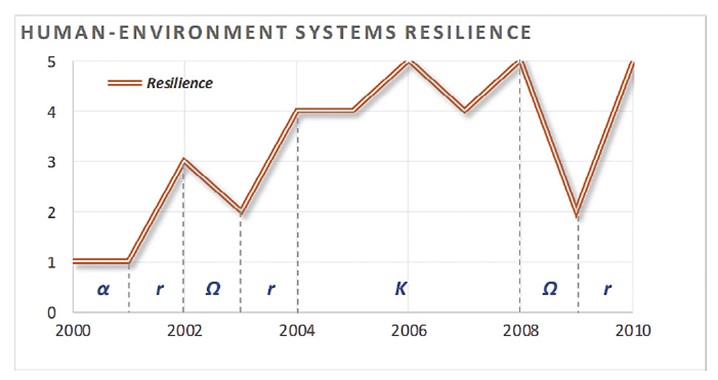
Fig. 6. Comprehensive resilience curve of human-environment systems (2000e2010).

