作者:Dai, MY; Liu, WW; Hong, HL; Lu, HL; Liu, JC; Jia, H; Yan, CL
影响因子:3.24
刊物名称:MARINE POLLUTION BULLETIN
出版年份:2018
卷:126 页码:86-92
Phosphorous (P) is an essential element that mediates various stresses in plants. In this study, the effects of P on polysaccharides in the root cell walls of two hydroponically cultivated mangrove seedlings (A. marina and K. obovata) that differ in Cd accumulation ability were examined in the context of Cd stress. The results showed that A. marina exhibited a higher degree of tolerance to Cd than K. obovata. In both mangrove seedlings, pectin and hemicellulose 1 increased significantly with increasing P levels, the effects of which were greater in A. marina under Cd stress. In addition, cell wall pectin methylesterase (PME) activity was markedly increased in the presence of Cd and P compared with Cd alone. These effects were more pronounced in A. marina than in K. obovata. Taken together, the results of this study provide further insight into the mechanisms of P-mediated alleviation of Cd stress in mangrove seedlings.
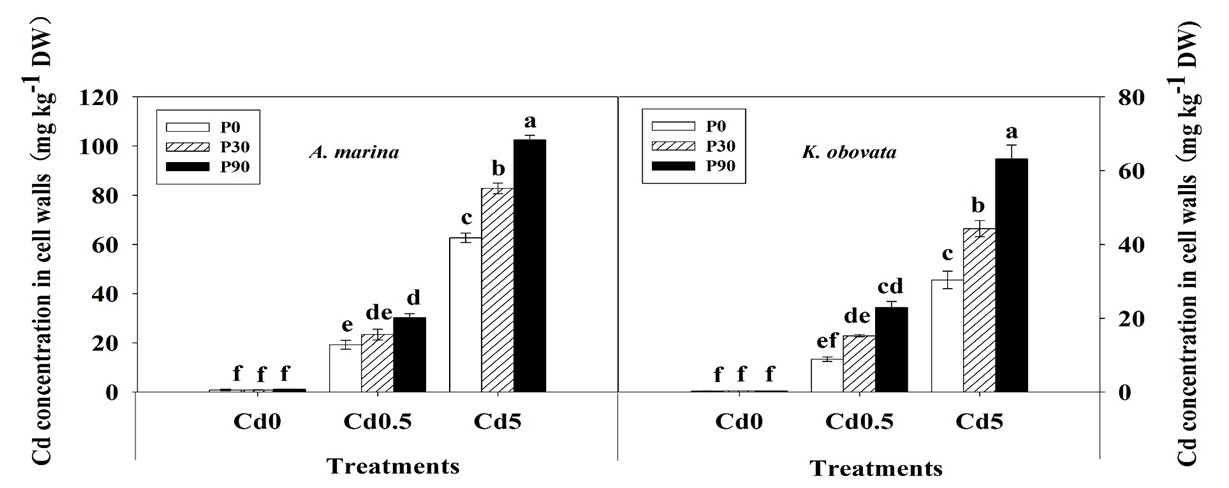
Figure 3. Effects of P on Cd concentrations in root cell walls of A. marina and K. obovata seedlings grown in nutrient solutions containing different concentrations of P and Cd for month.

