作者:Lin, YS; Fan, J; Yu, JF; Jiang, S; Yan, CL; Liu, JC
影响因子:3.24
刊物名称:MARINE POLLUTION BULLETIN
出版年份:2018
卷:135 页码:1174-1182
Sulfur and iron are abundant and have close, complex interactions with the biogeochemical cycle of arsenic (As) in mangrove ecosystems. A hydroponic experiment was conducted to investigate the influences of variable SO42- and Fe2+ supplies on radial oxygen loss (ROL), iron plaque formation and As translocation in Avicennia marina upon exposure to As(III). The results indicate that A. marina is an As-tolerant plant, the application of iron and sulfur not only showed positive growth effects but also induced much higher amounts of ROL-induced iron plaque formation on root surfaces. The presence of iron plaque remarkably improved the proportion of As sequestration near this area but consequently reduced the proportion of As translocation in root. Therefore, it is concluded that iron plaque may act as a barrier for protection against As, and iron and sulfur play important roles in controlling the growth and translocation of As in A. marina seedlings.
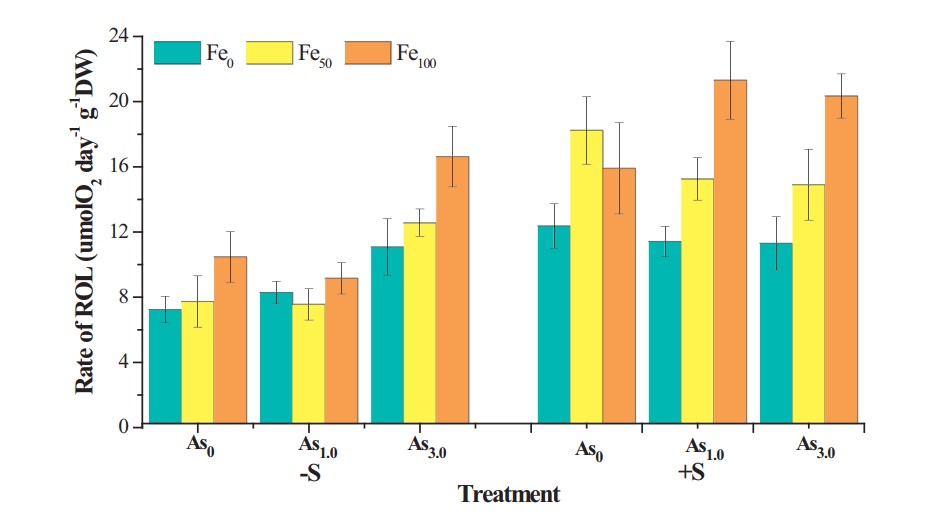
Figure 4. Rates of radial oxygen loss (ROL) from A. marina seedlings roots grown in various supplies of arsenic, sulfur and iron.

