作者:Wang, YC; Shen, C; Wang, CG; Zhou, YX; Gao, DX; Zuo, ZH
影响因子:4.43
刊物名称:CHEMOSPHERE
出版年份:2018
卷:191 页码:7-16
The water-soluble fraction (WSF) of crude oil plays an important role in the toxicity of crude oil in aquatic environments. Heavy metals, such as lead (Pb) are also important environmental contaminants, which can reach aquatic systems via the effluents of industrial, urban and mining sources. In the present study, we investigated whether maternal and embryonic exposure to the WSF (5, 50 μg/L) or Pb (10, 100 μg/L) could induce behavioral abnormalities in zebrafish. Our results showed that maternal and embryonic exposure to the WSF (5, 50 μg/L) and Pb (10, 100 μg/L) induced swimming activity alterations in larval and juvenile zebrafish. In 15 days post-fertilization (dpf) larval zebrafish, the distance moved was significantly increased in the groups treated with the WSF (5, 50 μg/L), but the angular velocity and turn angle were decreased after treatment with the WSF (5, 50 μg/L) or Pb (10, 100 μg/L). In 30 dpf juvenile zebrafish, the distance moved was markedly decreased in both groups treated with the WSF (5, 50 μg/L) and the Pb (10 μg/L) group, but the percentage of zebrafish moving up and the inter-fish distance of two juvenile fish were increased after treatment with the WSF (5, 50 μg/L) or Pb (10, 100 μg/L). Maternal and embryonic exposure to the WSF (5, 50 μg/L) or Pb (10, 100 μg/L) likely impaired the brain neurons growth and induced behavioral abnormalities in the larval and juvenile zebrafish. Furthermore, the expressions of some key genes, which were associated with calcium channels, behavioral development or the metabolism of environmental contaminants, were changed.
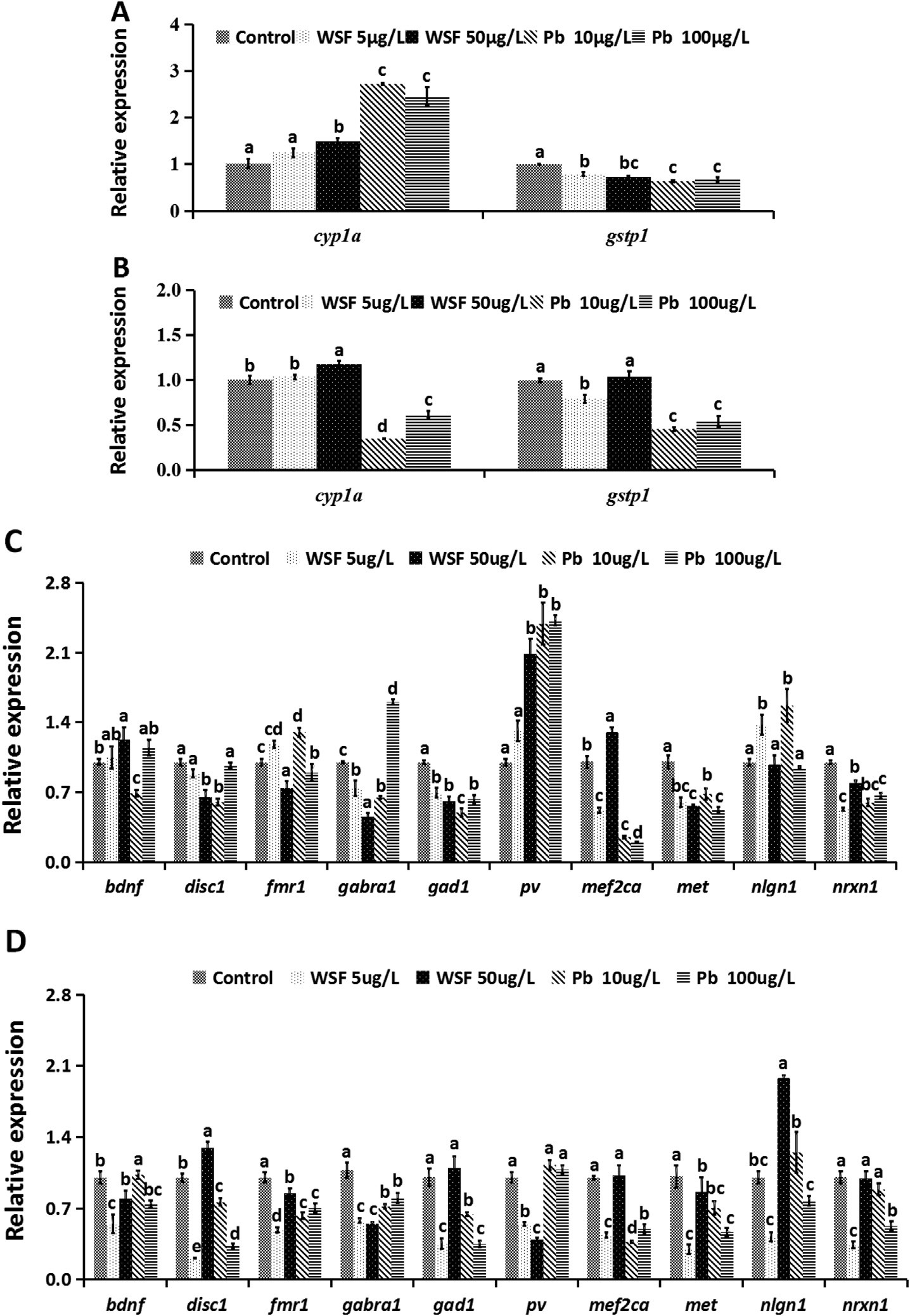
Figure 4. Relative mRNA expression of cyp1a and gstp1 (A and B) and of bdnf, disc1, fmr1, gabra1, gad1, pv, mef2ca, met, nlgn1 and nrxn1 (C and D) of 15 dpf and 30 dpf zebrafish exposed to the WSF or Pb before spawning and fertilization. (A) and (C) show the relative mRNA expression of genes of the 15 dpf zebrafish larvae. (B) and (D) show the gene expressions of the 30 dpf juvenile zebrafish. Data (mean ± SE) were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by the Duncan test (n ¼ 6 per group). Treatments not sharing a common letter are significantly different at P < 0.05.

