作 者:Cao, D; Cao, W; Yu, K; Wu, G; Yang, J; Su, X; Wang, F
影响因子:2.939
刊物名称:JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH-OCEANS
出版年份:2017
卷: 122(5) 页码: 4431-4443Coral reefs have suffered remarkable declines worldwide. Nutrient overenrichment is considered to be one of the primary local causes. The Luhuitou fringing reef in southern China is a well-known tourist destination that is subject to enormous coastal renovation. The mean d13C, d15N value, and carbon over nitrogen ratio (C/N) of particulate organic matter were 221.5661.94&, 7.0463.81&, and 5.8161.86, respectively, suggesting mixed sources of carbon and nitrogen. The IsoError calculations suggested that marine phytoplankton and marine benthic algae dominated the majority of carbon sources, while anthropogenic and terrestrial organic nitrogen dominated the nitrogen sources. A tendency toward greater terrestrial detritus and anthropogenic-derived discharges was found during dry seasons and greater marine-derived organic matter during wet seasons. These results demonstrated the existence of anthropogenic influences and high dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations and C/N ratios. Anthropogenic nutrient discharge moderated nitrogen limitation, whereas phosphorus became more important to the reef ecosystem. Despite the marine carbon sources dominated, freshwater and terrestrial-derived organic carbon sources were also very important. Meanwhile, anthropogenic and terrestrial organic nitrogen sources were dominant. Therefore, pollution from more extensive region and anthropogenic activities from riverine sewage discharges adjacent to reefs should be focused to effectively reduce human-derived nutrients on reefs.
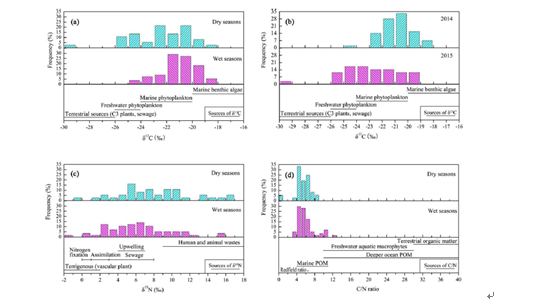
Fig. 10.Frequency distributions of (a) d13C values, (b) annual d13C values, (c) d15N values, and (d) C/N ratios with various published nutrient sources from various nutrient sources woldwide.

