作 者:Dai, MY; Lu, HL; Liu, WW; Jia, H; Hong, HL; Liu, JC;Yan, CL
影响因子:3.743
刊物名称:ECOTOXICOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
出版年份:2017
卷:139 页码: 272-279
Mangrove ecosystems are vulnerable to environmental threats. In order to elucidate the effect of phosphorus (P) on cadmium (Cd) tolerance and physiological responses in mangroves under Cd stress, a mangrove specie with salt exclusion Kandelia obovata and a specie with salt secretion Avicennia marina were compared in a hydroponic experiment. The results showed that most Cd was accumulated in mangrove roots and that P addition induced Cd immobilisation in them. Cd stress significantly increased malonaldehyde content, whereas P significantly decreased malonaldehyde in mangroves. Phosphorus positively regulated the photosynthetic pigment, proline content and synthesis of non-protein thiols, glutathione and phytochelatins in the leaves under Cd stress conditions. The results suggest different adaptive strategies adopted by two mangroves in a complex environment and A. marina showed a stronger Cd tolerance than K. obovata. The study provides a theoretical basis for P mediated detoxification of Cd in mangrove plants.
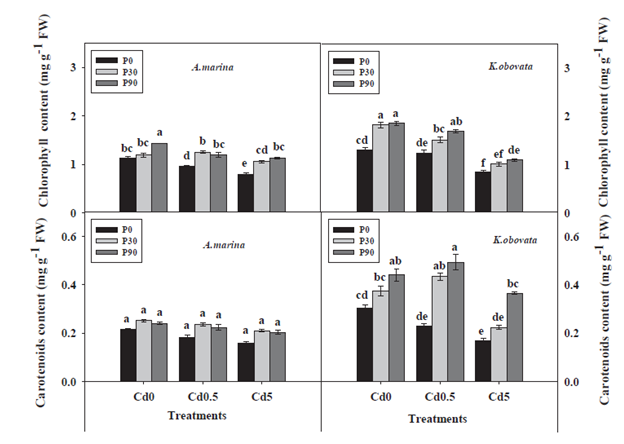
Fig. 18.Effect of different Cd and P treatments on photosynthetic pigments in leaves of A. marina and K. obovata.

