作 者:Lin, KD; Lao, WJ; Lu, ZJ; Jia, F; Maruya, K; Gan, J
影响因子:4.9
刊物名称:SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT
出版年份:2017
卷:599 页码: 364-371
The coupling of disposable solid-phase microextraction (SPME) with performance reference compounds (PRCs) has been recently introduced to measure time-averaged freely dissolved concentrations (Cfree) of hydrophobic organic contaminants in sediments under laboratory conditions. To explore the use of PRC-SPME for in situ sampling in seawater, disposable PDMS fibers (35-μmand 100-μmcoating) preloadedwith stable isotope labeled analogues as PRCs were deployed at six stations (each with three depths) in the open ocean of the Palos Verdes Shelf (CA, USA) Superfund site for 33 d to measure Cfree of DDT and its degradates. The observed values of fractional equilibration (feq) of PRCs were mostly b0.85, suggesting nonequilibrium conditions at the end of deployment. The observed feqs for the samplers variedwith compound, sampling station and depth, validating the need for calibration to derive accurate Cfree. The Cfree values of DDE and DDD determinedwith PRC-SPME were in good agreement with those previously measured by in situ large-volume water sampling or polyethylene devices. The highest Cfree in seawater 5moff the ocean floorwas 750 pg L−1 for o,p′-DDE, 2170 pg L−1 for p,p′-DDE, 24 pg L−1 for o,p′-DDD, and 75 pg L−1 for p,p′-DDD. Results of this study demonstrated the feasibility and advantages of using disposable PDMS fiber coupled with PRCs for in situ sampling.
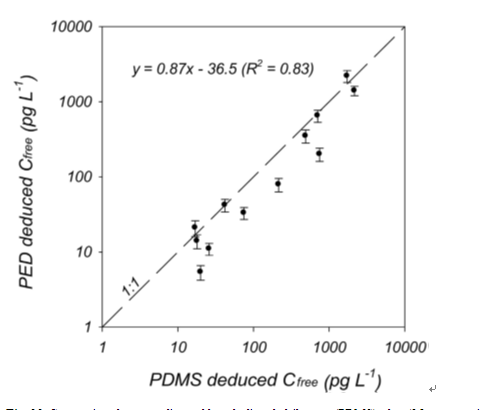
Fig. 22.Comparison between disposable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) fiber (35-μm coating) and low-density polyethylene device (PED) deduced Cfree for o,p′-DDE, p,p′- DDE, o,p′-DDD, and p,p′-DDD in the water column 5 m above bottom (stations BA4C, BA8C, and BA9C). PE-deduced data are from Fernandez et al. (2012). Both PDMS and PE deduced data were calibrated with performance reference compounds (PRCs).

