作 者:Li, Y., Zhu, H., Lei, X.Q., Zhang, H.J., Guan,C.W., Chen, Z.R., Zheng, W., Xu, H., Tian, Y., Yu, Z.M., et al. 影响因子:
刊物名称:Journal of Hazardous Materials
出版年份:2015
卷:290 页码:87-95
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) could be deemed hazardous materials in aquatic environment.Alexandriumtamarenseis a toxic HAB causing alga, which causes serious economic losses and health problems. In thisstudy, the bacteriumDeinococcusxianganensisY35 produced a new algicide, showing a high algicidaleffect onA. tamarense.The algicidal compound was identified as deinoxanthin, a red pigment, based onhigh resolution mass spectrometry and NMR after the active compound was isolated and purified. Deinoxanthin exhibited an obvious inhibitory effect on algal growth, and showed algicidal activity againstA.tamarensewith an EC50of 5.636μg/mL with 12 h treatment time. Based on the unique structure and characteristics of deinoxanthin, the content of reactive oxygen species (ROS) increased after 0.5 h exposure,the structure of organelles including chloroplasts and mitochondria were seriously damaged. All theseresults firstly confirmed that deinoxanthin as the efficient and eco-environmental algicidal compoundhas potential to be used for controlling harmful algal blooms through overproduction of ROS.
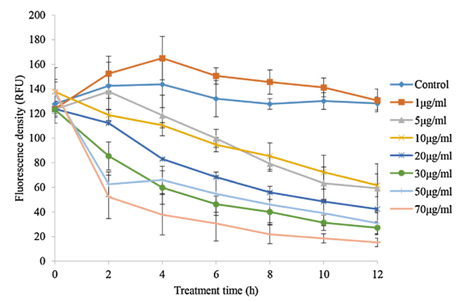
Fig. 4.Algicidal effects of different concentrations of deinoxanthin onA. tamarense.

