Xiaowei Zheng, Bangzhou Zhang, Jinlong Zhang, Liping Huang, Jing Lin, Xinyi Li, Yanyan Zhou, Hui Wang, Xiaoru Yang, Jianqiang Su, Yun Tian, Tianling Zheng.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2013. 97:9207– 9215
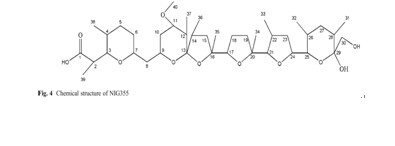
A strain O4-6, which had pronounced algicidaleffects to the harmful algal bloom causing alga Phaeocystisglobosa, was isolated from mangrove sediments in theYunxiao Mangrove National Nature Reserve, Fujian,China. Based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence and morphological characteristics, the isolate was found to be phylogenetically related to the genus Streptomyces and identified asStreptomyces malaysiensis O4-6. Heat stability, pH tolerance, molecular weight range and aqueous solubility weretested to characterize the algicidal compound secreted fromO4-6. Results showed that the algicidal activity of thiscompound was not heat stable and not affected by pHchanges. Residue extracted from the supernatant of O4-6fermentation broth by ethyl acetate, was purified bySephadex LH-20 column and silica gel column chromatography before further structure determination. Chemicalstructure of the responsible compound, named NIG355,was illustrated based on quadrupole time-of-flight massspectrometry (Q-TOF-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR) spectra. And this compound showed a strongeralgicidal activity compared with other reported algicides.Furthermore, this article represents the first report of analgicide against P. globosa, and the compound may bepotentially used as a bio-agent for controlling harmful algalblooms.