Fei-Hua Wu, Juan Chen , Ting-Wu Liu, Zhen-Ji Li, Juan Chen, Lei Chen, Shao-Hua Guan, Tong-Yang Li, Xue-Jun Dong, Janet Patton, Hai-Lei Zheng.Plant Ecol,2013.214: 557–569.
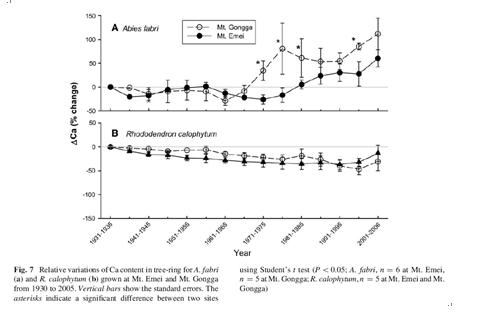
The correlation between forest decline andcalcium (Ca) depletion under long-term acid depositionremains elusive in China due to the high level ofCa deposition. We compared two species (Abies fabriand Rhododendron calophytum) for their growthpattern and base elements concentration in bothpolluted (Mt. Emei) and unpolluted (Mt. Gongga)sites in Sichuan, southwestern China. A. fabri grown atMt. Emei had poorer crown condition, slower radialgrowth rate, and lower seedling density under longtermacid deposition, which correlated closely with thereduced Ca concentration in foliage and tree-ring, incomparison with those at Mt. Gongga. In contrast, R.calophytum showed a stable Ca level and thusdisplayed normal growth between the two sites. Thedifferential capability of these two species to acclimateto poor Ca environment is one of the keys tounderstanding the long-term ecological effect ofchanging atmospheric acid and Ca deposition in thesubalpine forest in southwestern China.