Jun-Rong Liang, Xin-Xin Ai, Ya-Hui Gao, Chang-Ping Chen.J Appl Phycol, 2013. 25: 477-484.
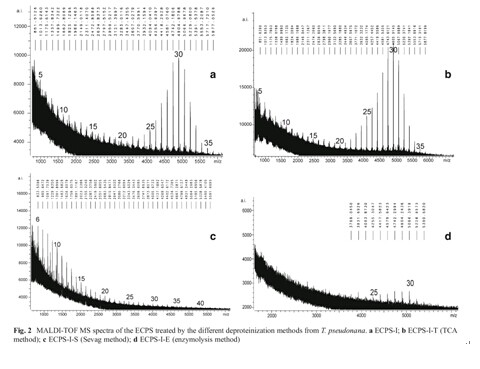
The extracellular polysaccharides (ECPS) releasedby diatoms have significant roles in marine ecosystems andhave potential applications including drug-discovery and biopharmaceuticalprecursors. In this study, matrix-assisted laserdesorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry(MALDI-TOF MS) technology was used in the structuralanalysis of the ECPS released byThalassiosira pseudonana(Bacillariophyta). Three different deproteinization methods,the Sevag method, the trichloroacetic acid (TCA) method,and the enzymolysis method, were compared in the purificationof ECPS. Our results suggested that TCA was the bestdeproteinization method among the three methods for subsequentMALDI-TOF MS investigation because of its highECPS yield, protein removal ability and reliable MALDI-TOFMS fingerprint. The degree of polymerization (d.p.)profiles, the molecular weight of the ECPS and the distributionpattern of the polymers with different molecular masswere described from the MALDI-TOFMS spectra. This workrepresents the whole-level composition of the ECPS releasedby the diatom and has improved our knowledge of the structuralcharacterization of ECPS.