Zhang JL, ZH Zuo, YQ Wang, A Yu, YX Chen and CG Wang.Chemosphere, 2011. 82: 437-442.
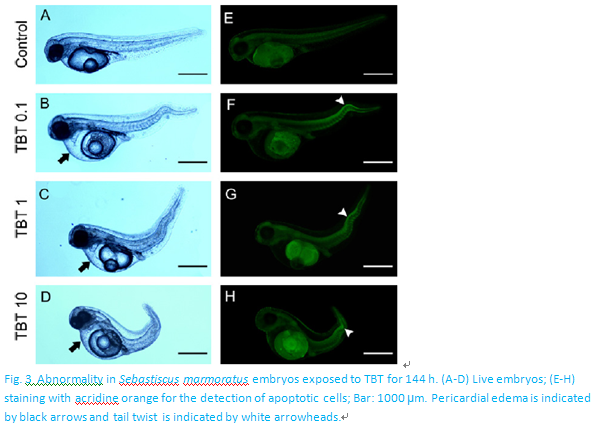
Tributyltin (TBT) is a ubiquitous marine environmental contaminant characterized primarily by its reproductive toxicity. However, the embryotoxicity of TBT has not been extensively described, especially in fishes. The aim of this study was to investigate the developmental toxicity of waterborne TBT at environmental levels (0, 0.1, 1, and 10 ng L-1as Sn) onSebastiscus marmoratusembryos. Our study showed that TBT reduced the hatchability and caused apparent morphological abnormalities including dorsal curvature, severely twisted tails and pericardial edema. In addition, localized apoptosis was found in the tail regions of embryos after TBT exposure. The study provided a possible mechanistic link between apoptosis and TBT-induced twisted tails abnormality. TBT exposure induced retinoid X receptor a expression in S. marmoratus embryos at the 0.1 and 1 ng L-1group, which would be responsible for the increasing apoptotic cells induced by TBT. The results of the present study have widespread implications for environmental ecological assessment, management and the etiology of developmental defects.