Lin Y.M.* Liu X.W., Zhang H, Fan H.Q., Lin G.H.Plant and Soil, 2010. 326:469–479.
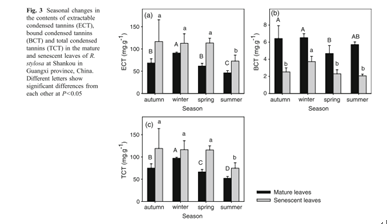
Despite a growing knowledge of nutrient limitation for mangrove species and how mangroves adapt to low nutrients, there is scant information about the relative importance of N:P ratio and leaf phenolics variability in determining nutrient conservation. In this study, we evaluated possible nutrient conservation strategies of a mangroveRhizophora stylosaunder nutrient limitation. 1. The leaf nutrient concentrations ofR. stylosachanged with season, with the highest N concentration in winter and the highest P concentration in spring for both mature and senescent leaves. Leaf N and P concentrations decreased significantly during leaf senescence. Based on N:P ratiosR. stylosaforest was N-limited. Accordingly, the nitrogen resorption efficiency (NRE) was significantly higher than phosphorus resorption efficiency (PRE) for theR. stylosaleaves during leaf senescence. The NRE and PRE both reached the highest in the autumn. Average N and P concentrations in the senescent leaves were 0.15% and 0.06% forR. stylosa, respectively, indicating a complete resorption of N and an incomplete resorption of P. There was a significant negative correlation between nitrogen resorption proficiency (NRP) and NRE, meanwhile phosphorus resorption proficiency (PRP) and PRE correlation was also highly significantly. 2.R. stylosaleaves contained relatively high tannin level. Total phenolics, extractable condensed tannins and total condensed tannins contents increased during leaf senescence, and changed between seasons. The lowest concentrations of total phenolics, extractable condensed tannins and total condensed tannins occurred in summer, total phenolics concentrations were inversely related to nitrogen or phosphorus concentrations. 3. Our results confirmed that resorption efficiency during leaf senescence depends on the type of nutrient limitation, and NRE was much higher than PRE under N-limited conditions.R. stylosaforest developed several nutrient conservation strategies in the intertidal coastline surroundings, including high nitrogen resorption efficiency, low nutrient losses and high tannins level.