Zhou X.P., Fang W.Z., and Chen X.L.Journal of Ornithology. 2009. DOI: 10.1007/s10336-009-0470-7.
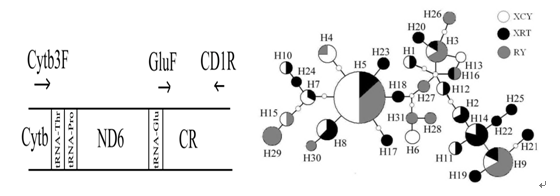
Abstract: The genetic diversity and population structure of the vulnerable Chinese Egret (Egretta eulophotes) were surveyed in the present study from three archipelagoes that cover the most south to the very north across the Chinese distribution range of this species, using a 433-bp fragment of the mitochondrial control region (CR). Among 90 individual samples, 31 different haplotypes were defined by 30 polymorphic sites. Overall haplotype diversity, nucleotide diversity and mean sequence divergence (p-distance) of this Egret were 0.920, 0.0088 and 1.11%, respectively. NJ tree and parsimony network for the CR haplotypes of the Chinese Egret showed little genetic structure and analysis of molecular variance indicated low but significant genetic differentiation (haplotype-based ΦST = 0.03267, P < 0.05 and distance-based φst="0.04194," p < 0.05) among populations. the significant fu’s fs tests (fu’s fs="-16.946," p < 0.01) and mismatch distribution analysis (τ="4.463," ssd="0.0081," p="0.12)" suggested that the low genetic differentiation and little geographical structure of the genetic differentiation might be explained by the population expansion. the mantel test (haplotype-based fst, r="0.639," p="0.34" and distance-based fst, r="0.947," p="0.15)" suggest that the significant genetic differentiation among populations was likely due to isolation by distance.