Wu G.J., Cao W.Z., Wang F.F., Su X.L., Yan Y.Y. and Guan Q.S.. 2019. Science of the Total Environment, 661: 130-137.
An increase in riverine nutrient fluxes significantly influences the estuarine ecosystem. This study collected nutrient data in most of China's rivers from 1963 to 2015 to estimate the nutrient fluxes from major rivers and analyze interannual variability of nutrient fluxes and estuarine environmental effects. The results showed that the nutrient fluxes from the Yangtze River increased annually from 1963 to 2012. The trend of nutrient fluxes from the Yellow River was consistent with that from the Jiulong River, i.e., nutrient fluxes increased from 1998 to 2007 and then decreased. The areal nutrient fluxes from China's major rivers were higher than those from major world rivers, while the areal nutrient yield rates per capita were lower than those from major world rivers. We also found that China's estuaries were predominantly phosphorus-limited and slowly moving toward lower dissolved silica over dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DSi:DIN) ratios with time. Meanwhile, the nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in most of China's estuary systems was moving toward a higher incidence of phosphorus and silicon limitations as a result of increased DIN fluxes, and this would likely alter phytoplankton communities. Furthermore, the decreases in the DSi:DIN ratio and dissolved silica over dissolved inorganic phosphate (DSi:DIP) ratio, and the increases in both DIN and DIP fluxes, caused increased red tide blooms.
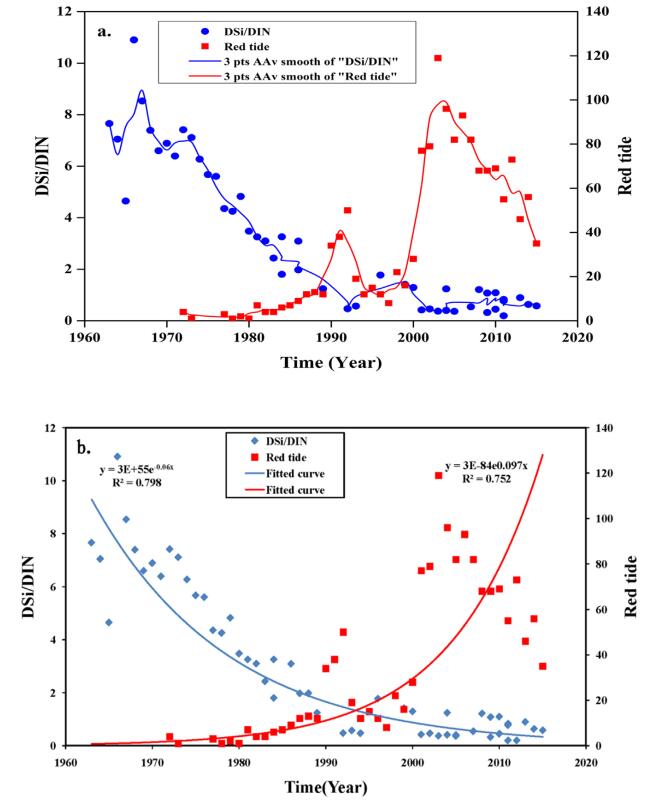
Figure 1. Variation of red tide occurrence, and DSi:DIN at China's near shore over the years.

