Wu Q.L., Zheng T.Y., Simpson S.L., Tan Q.G., Chen R. and Xie M.W.. 2021. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(19):13005-13013.
The direct measurement of particulate contaminant bioavailability is a challenging aspect for the environmental risk assessment of contaminated sites. Here, we demonstrated a multi-metal stable-isotope-enriched bioassay to simultaneously measure the bioavailability of Cd, Cu, and Zn in naturally contaminated sediments following differing periods of resuspension treatment. Freshwater filter-feeding clams were pre-labeled with the isotopes 114Cd, 65Cu, and 68Zn to elevate isotope abundances in their tissues and then exposed to metal-contaminated suspended sediments. The assimilation of sedimentassociated metals by clams would decrease the isotope ratios (Cd114/111, Cu65/63, and Zn68/64) in tissues, providing a direct measurement of metal bioavailability. For the sediments tested here, the method revealed bioavailable cadmium and non-bioavailable copper in sediments but was inconclusive for zinc. With a longer resuspension time, the bioavailability of particulate cadmium increased, but that of copper was unaffected. Metal bioavailability predicted using traditional wet-chemical extraction methods was inconsistent with these findings. The study indicated that multi-metal stableisotope-enriched bioassay provides a new tool for directly assessing metal bioavailability in sediments, and this method is amenable for use in in situ assessments.
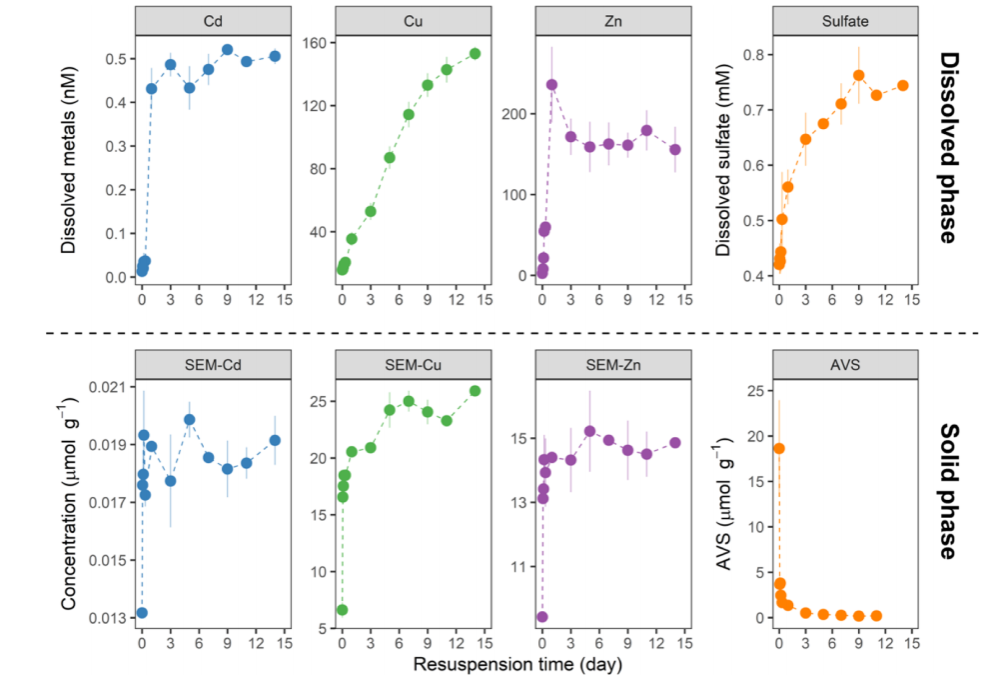
Figure 1. Release of dissolved constituents and changes in metal speciation during the resuspension. Top: temporal release of dissolved Cd, Cu, Zn, and sulfate. Bottom: temporal changes in AVS and SEM−Cd, −Cu, and −Zn. The symbols in the figure represent the mean of the triplicate experiments, while the error bars represent standard deviation from triplicate experiment results.

