Hamid Mohammad Al-Gabra,
Tianling Zhengb,Xin Yua,Science of the Total Environment,
2013. 463–464:525– 529
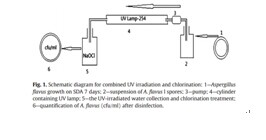
The disinfection process for inactivating
microorganisms at drinking water treatment plants is aimed for safety
ofdrinking water for humans from a microorganism, such as bacteria, viruses,
algae, fungi by using chlorination,ozonation, UV irradiation, etc. In the
present study, a combination of two disinfectants, UV irradiation followedby
chlorination, was evaluated for inactivating Aspergillus flavus under low contact
time and low dosage of UVirradiation. The results indicated an inverse
correlation between the inactivation of A. flavus by using UV irradiation only
or chlorination alone. By using UV radiation, the 2 log 10 control of A. flavus
was achieved after 30 s ofirradiation, while chlorination was observed to be
more effective than UV, where the 2 log was achieved at chlorine concentration
of 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 mg/l, in contact time of 60, 5, 1 and 1 min, respectively.
However, combineduse (UV irradiation followed by chlorination) was more
effective than using either UV or chlorination alone; 5 sUV irradiation
followed by chlorination produced 4 log 10 reduction of A. flavus at chlorine
concentrations of 2 and3 mg/l under a contact time of 15 min. The results
indicated that efficiency of UV irradiation improves whenfollowed by
chlorination at low concentrations.
返回

