作 者:Zhang, YB;Bai, MD; Chen, C; Meng, XY; Tian, YP; Zhang, NH; Yu, Z.
影响因子:2.056
刊物名称:Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing
出版年份:2013
卷:33 期:4 页码:751-763
文章摘要:
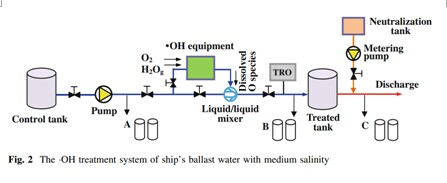
A novel discharge mode consisting of alternate discharge of a micro-streamer and micro-glow was developed to induce the formation of ·OH radicals in ballast water. A series of ·OH killing experiments were then conducted using medium salinity ballast water. Five species of algae from three different phyla and three kinds of bacteria were killed by ·OH radicals in compliance with the D-2 ballast water standard of International Maritime Organization. Moreover, thechlorophyll-awas fully discolored when the total reactive oxidants was 2.5 mg/L, indicating that the algae had died. Overall, the quality of medium salinity ballast water with heavy pollution was greatly improved. These results indicate that the use of ·OH radicals is an effective method for the treatment of ship’s ballast water.