Xiaojia Huang,
Yulei Wang, Yi Liu, Dongxing Yuan.Journal of Separation Science,2013.
36: 3210–3219
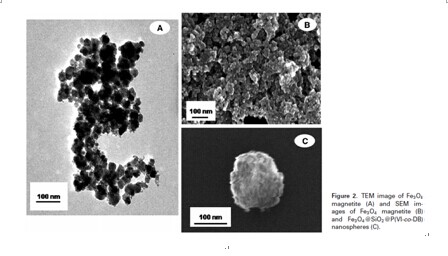
Nanosized
spherical magnetic poly(vinylimidazole-co-divinylbenzene) particles were
synthesizedand used as a sorbent for the enrichment of trace fluoroquinolones
(FQs) fromenvironmental water samples. A suspension polymerization procedure
was used to preparethe sorbent. The magnetic sorbent was characterized by SEM,
transmission electronmicroscopy, elemental analysis, and FTIR spectroscopy.
Analysis of enrofloxacin, marbofloxacin,fleroxacin, lomefloxacin, and
sparfloxacin in environmental water samples bythe combination of the magnetic
sorbent and HPLC with diode array detection was selectedas a paradigm for the practical
application of the new adsorbent. Several extractionconditions, including
desorption solvent, extraction and desorption time, pH value, andionic strength
in sample matrix, were optimized. Results showed that the new sorbent hadhigh
affinity for FQs and could be used to extract them effectively. Under the
optimumconditions, low detection (S/N = 3) and quantification (S/N = 10) limits
were achieved forthe target analytes, within the ranges of 0.20–1.46 and
0.68–4.84 _g/L, respectively. Methodrepeatability was achieved in terms of
intra- and interday precisions, indicated by the RSDs,which were both
<10 .0%. the method also showed good linearity, simplicity, practicality,and
environmental friendliness for the extraction of FQs. Finally, the developed method
wassuccessfully applied to the determination of FQs in lake water, surface
water, and reservoirwater samples. Acceptable recoveries of spiked target
compounds in these water sampleswere in the range of 52.1–104.5%.
返回

