Ruifeng Zhang,
Chongling Yan,Jingchu Liu.Journal of Coastal Research.2013. 29(6): 1341-1350
To examine the influence of the mangrove environment on the
distribution of rare eartb elements (REE) in estuarinesediments, surface and
core sediments were collected from regions of mangrove forest, forest fringe,
and adjacentmudflat in the Zhangjiang estuary, SE China. Concentrations of REE
were determined in surface sediments and coresamples using inductively coupled
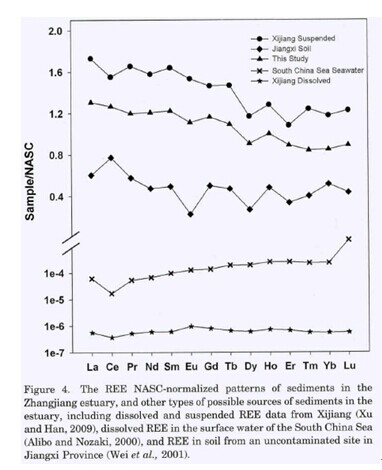
plasma mass spectrometry. Light REE were more enriched than heavy REE, with
arelatively weak negative europium anomaly with respect to the North American
shale composite in sediments of theZhangjiang estuary. Significant differences
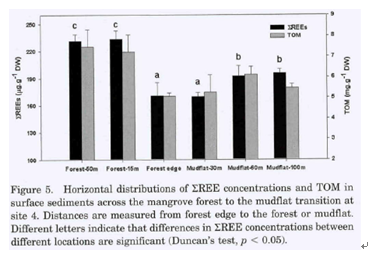
for REE were found among sampling sites and locations, following the
ordermangrove forest, to forest edge, to mudflat. The main source for REE in
the estuary is tbe weathered continentalmaterials from the Zhangjiang River
drainage hasin. The mangrove environment affected the physicochemical
featuresand thus affected the REE spatial distributions in sediments. Vertical
REE distributions in core samples were altered bymangrove root activity.
Mangroves played a significant role in controlling the horizontal and vertical
distribution of REEin sediments of the Zhangjiang estuary.
返回

