Xiao-Xin Chen, Jian Zhang,
Wei-Ming Chai, Hui-Ling Feng,Zhi-Hao Xiang, Dong-Yan Shen, Qing-Xi Chen.International
Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2013. 62: 726-733.
In the present work, we investigated the inhibitory effects of
amoxicillin, a bacteriolytic -lactam antibiotic drug, on the rate of monophenol
hydroxylation and o-diphenol oxidation catalyzed by mushroomtyrosinase. The
results showed that amoxicillin could inhibit both monophenolase and
diphenolase activities. For monophenolase activity, the inhibition on reaction
rate was dose-dependent, while the influenceon lag period was not obvious. For
diphenolase activity, amoxicillin was found to be a reversible inhibitor,with
an IC50value of 9.0±1.8
mM. Kinetics analysis showed that amoxicillin was a mixed type inhibitorof the
enzyme with KIand KISvalues of 8.30 mM and 44.79 mM, respectively. Further, the
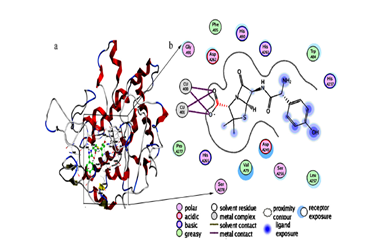
molecularmechanism underlying the inhibition of tyrosinse by amoxicillin was
investigated by means of fluorescence quenching and molecular docking
techniques. The results showed that amoxicillin could formstatic interaction
with the catalytic pocket of the enzyme through the interaction of amoxicillin
with thedicopper irons and amino acid residues in the enzyme active center. Our
results contributed to the usageof amoxicillin as a potential tyrosinase
inhibitor in the field of medicinal industry and could also provideguidance in
the design of novel tyrosinase inhibitors.
返回

