Wang MH, YY Wang, J Wang,L Lin,HS Hong,DZ Wang.Aquatic Toxicology, 2011. 103: 129-139.
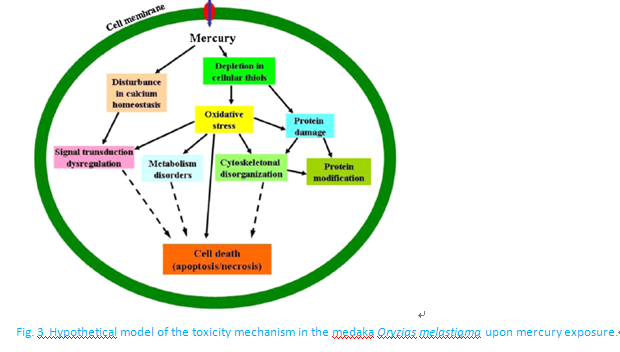
Mercury is a widespread and persistent pollutant occurring in a variety of forms in freshwater and marine ecosystems. Using the proteomic approach, this study examined the protein profiles of the medaka (Oryzias melastigma) liver and brain exposed to an acute mercuric chloride (HgCl2) concentration (1000 μg/L) for 8 h. The results showed that acute exposure of medaka to inorganic mercury enhanced metal accumulation in both the liver and brain, and a higher content of mercury was detected in the latter. Comparison of the two-dimensional electrophoresis protein profiles of HgCl2-exposed and non-exposed group revealed that altered protein expression was quantitatively detected in 20 spots in the brain and 27 in the liver. The altered protein spots were subjected to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization tandem time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis, with the resultant identification of 46 proteins. The proteins identified were involved in oxidative stress, cytoskeletonal assembly, signal transduction, protein modification, metabolism and other related functions (e.g. immune response, ionoregulation and transporting), highlighting the fact that inorganic mercury toxicity in fish seems to be complex and diverse. This study provided basic information to aid our understanding of the possible molecular mechanisms of acute inorganic mercury toxicity in aquatic organisms, as well as potential protein biomarker candidates for aquatic environmental monitoring.