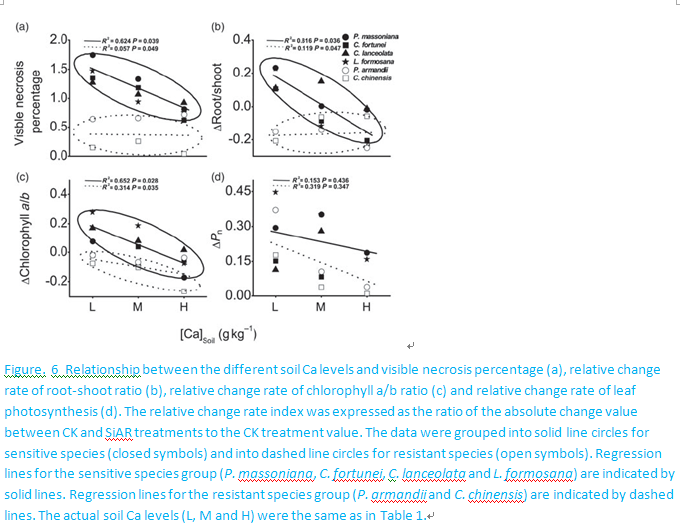
Liu TW, FH Wu, WH Wang, J Chen, ZJ Li, XJ Dong, J Patton, ZM Pei and HL Zheng.Tree Physiology, 2011. 31: 402-413.
We selected six tree species,Pinus massonianaLamb.,Cryptomeria fortuneiHooibr. ex Otto et Dietr.,Cunninghamia lanceolata(Lamb.) Hook.,Liquidambar formosana Hance,Pinus armandiiFranch. andCastanopsis chinensisHance, which are widely distributed as dominant species in the forest of southernChinawhere acid deposition is becoming more and more serious in recent years. We investigated the effects and potential interactions between simulated acid rain (SiAR) and three calcium (Ca) levels on seed germination, radicle length, seedling growth, chlorophyll content, photosynthesis and Ca content in leaves of these six species. We found that the six species showed different responses to SiAR and different Ca levels.Pinus armandiiandC. chinensiswere very tolerant to SiAR, whereas the others were more sensitive. The results of significant SiAR×Ca interactions on different physiological parameters of the six species demonstrate that additional Ca had a dramatic rescue effect on the seed germination and seedling growth for the sensitive species under SiAR. Altogether, we conclude that the negative effects of SiAR on seed germination, seedling growth and photosynthesis of the four sensitive species could be ameliorated by Ca addition. In contrast, the physiological processes of the two tolerant species were much less affected by both SiAR and Ca treatments. This conclusion implies that the degree of forest decline caused by long-term acid deposition may be attributed not only to the sensitivity of tree species to acid deposition, but also to the Ca level in the soil.