Zhou HC, YM Lin, SD Wei and NFY Tam.Food Chemistry, 2011. 129: 1710-1720.
The extract from mangosteen pericarp was separated into eight fractions, four by solvent extraction (hexane, FH; petroleum ether, FP; ethyl acetate, FE; water, FW) and the other four by fractionation on Sephadex LH-20 column (fractions F1, F2, F3, and F4). Phenolic compounds were identified as the major antioxidant components in each fraction. UV-VIS spectrum, reversed-phase HPLC-ESI-MS coupled with thiolysis, normal-phase HPLC-ESI-MS and MALDI-TOF-MS analyses complementally showed that the phenolic-rich fractions were condensed tannins with structural heterogeneity in monomer units, degree of polymerization and interflavan linkages. Mangosteen condensed tannins predominately contained procyanidins with a significant amount of propelargonidin but much lower signals of prodelphinidin. Eicosapentamers of condensed tannins were detected by MALDI-TOF-MS. Both B-type and A-type linkages were present. Condensed tannins fractions from mangosteen pericarp, especially fractions F3 and FE, can be explored as beneficial food antioxidants because of their high yields and potent antioxidant activities.
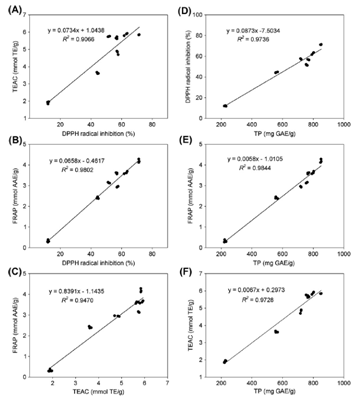
Fig. 1 Relationships among DPPH, FARP, and TEAC (A-C), and between antioxidant activity and total phenolics content (D-F).

