Chen NW, HS Hong.Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 2012. 4: 233-242.
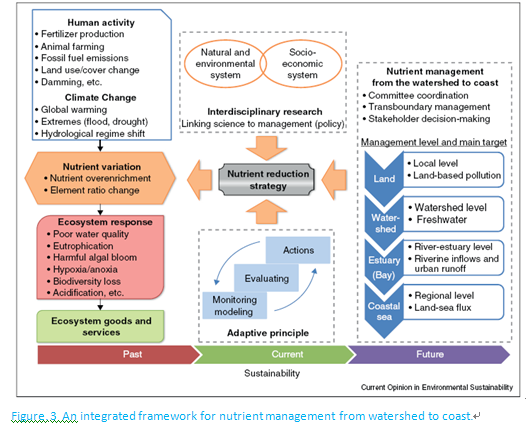
This paper is a brief review on nutrient variation (changes in element concentrations and ratios) and the associated aquatic ecosystem responses in the subtropical region. Human activities have significantly modified both the flux and the ratio of nutrients delivered to aquatic ecosystems. Climate perturbations influence the hydrological regime and enhance nutrient mineralization and transport from land to receiving waters. Changes in land use and damming have resulted in changes in the balance among nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon elements, thus increasing the risk of algal bloom. Nutrient variation and its ecological effects in the subtropical region could be more significant than in other areas because of rapid development and high population. Aquatic ecosystems respond to nutrient variation in complex and dynamic ways resulting in eutrophication, hypoxia/anoxia, acidification, and changes in phytoplankton and microbial communities. This review suggests that harmful algal bloom, jellyfish bloom, and serious pathogens are often associated with nutrient variations. The current challenges to scientific research and management include the facts that (1) the link between nutrient dynamics and ecosystem responses is poorly understood; (2) monitoring data to support modeling and management are scarce; (3) aquatic ecosystems are site-specific and/or situation-specific and are highly dynamic, giving greater complexity in research and management; and (4) the lack of regional coordination in traditional management causes transboundary gaps. To address these current challenges, an integrated management framework was proposed for effective nutrient management. Institutional arrangements should be developed to coordinate across multiple government agencies and other stakeholders from watershed to coast. The framework should integrate an interdisciplinary scientific approach and adaptive principles regarding nutrient management.