Wang F.; Tao Y.; Yang S. and Cao W. 2023. Journal of Soils and Sediments.
Purpose
Mangrove ecosystems which play a critical role in global C sequestration have recently become threatened by global warming and sea level rise. This study aimed to explore the responses of SOC mineralization and C pool stability in mangrove ecosystems to warming and flooding conditions.
Methods
Laboratory incubation and solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (13C-NMR) analysis were used to evaluated soil organic carbon (SOC) mineralization and stability under warming (ST), flooding (SW), warming in coincidence with flooding (SWT), and soil under normal temperature taken from a subtropical mangrove ecosystem in southeastern China.
Results
The cumulative SOC mineralization of ST increased by 24%, while SWT and SW decreased by 59% and 68% relative to CK, respectively. Furthermore, the 13C-NMR analysis showed that O-alkyl C was the dominant SOC chemical composition in all treatments (37.1–43.1%), followed by the aromatic C and alkyl C. The aromaticity index (AI) decreased, and the ratio of alkyl and O-alkyl to aromatic (Alip/Arom) increased in all treatments compared with CK, while the alkyl C/O-alkyl C ratio (A/O-A) and hydrophobicity index (HI) were higher for ST and SW but lower for SWT. Warming significantly facilitated SOC mineralization, and lowered SOC stability due to the high cumulative CO2-C production, while flooding had the opposite effects. However, warming in coincidence with flooding led to low SOC decomposition and a more recalcitrant substance.
Conclusion
The theoretical elevated CO2 release from mangrove soils under warming in coastal zones might be partially offset by prolonged flooding. The different effects on the chemical fractions, chemical compositions, and stability of the SOC pool in mangrove soil under warming and flooding might further complicate the research on coastal carbon sinks.
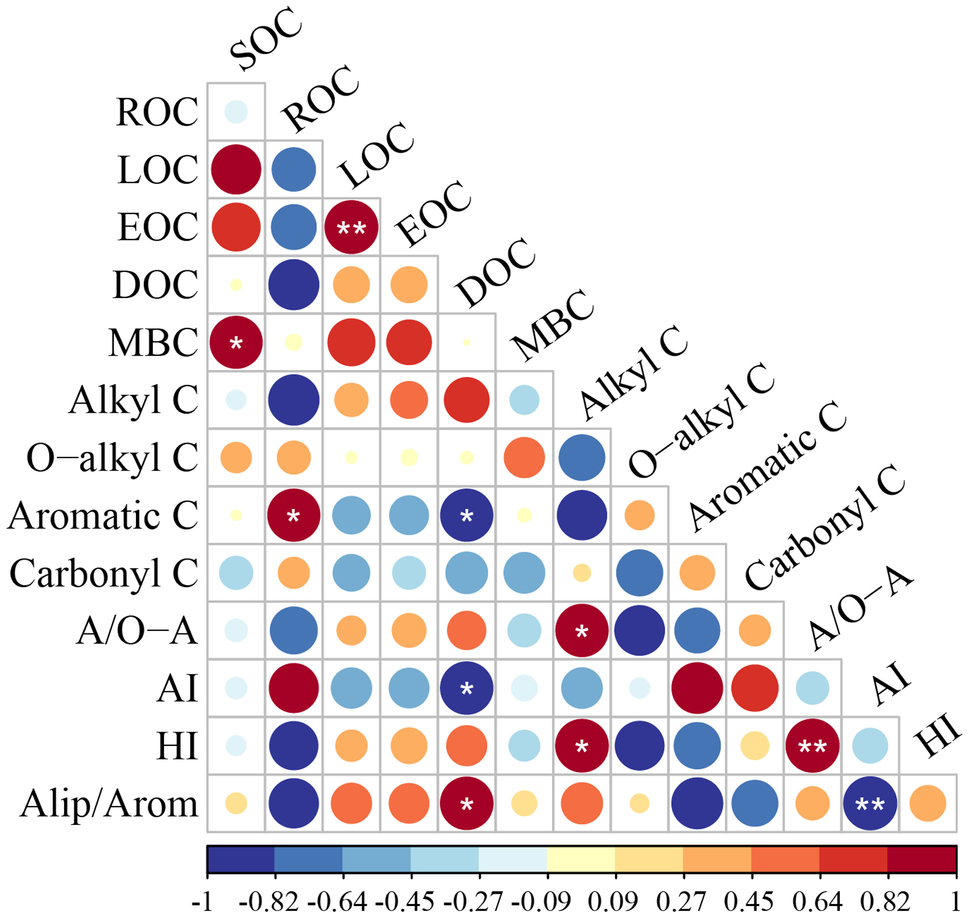
Correlations among the SOC fractions, compositions, and stability indices. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01

