Wu J.; Luo S. and Huang X. 2023. Chemical Engineering Journal 455.
Efficient co-extraction of phenylurea and sulfonylurea herbicides is challenging due to their distinct difference in chemical properties. In this connection, two novel monolith-based electrodes were prepared and employed as adsorbents of electric field assisted solid-phase microextraction (EFA-SPME) for simultaneously capturing phenylurea and sulfonylurea herbicides. Poly (vinylimidazole-co-ethylene dimethacrylate) monolith and poly (methylacrylic acid co-ethylene dimethacrylate/divinylbenzene) monolith were fabricated on the surface of stainless steel wires and utilized as anode and cathode of EFA-SPME, respectively. Various fabrication conditions and extraction parameters affecting the co-capture performance were studied systematically. Results revealed that the implement of electric field in adsorption duration, phenylurea and sulfonylurea herbicides were captured in cathode and anode, respectively. At the same time, the co-extraction performance was improved, adsorption and eluting durations were shortened. Combining with HPLC analysis technique, sensitive and reliable method for simultaneous monitoring of trace phenylurea and sulfonylurea herbicides in various environmental water and soil samples were developed. The limits of detection of phenylureas in water and soil samples were 0.0047–0.014 μg/L and 0.059–0.18 μg/kg, respectively. The corresponding values of sulfonylureas in water and soil sample were 0.011–0.015 μg/L and 0.099–0.19 μg/kg, respectively. In addition, the detailed extraction mechanism under electric field was studied. Finally, the practicality of established method was evaluated by successfully quantifying studied analytes at trace contents in environment water and soil samples, and confirmatory experiments were utilized to confirm the method accuracy.
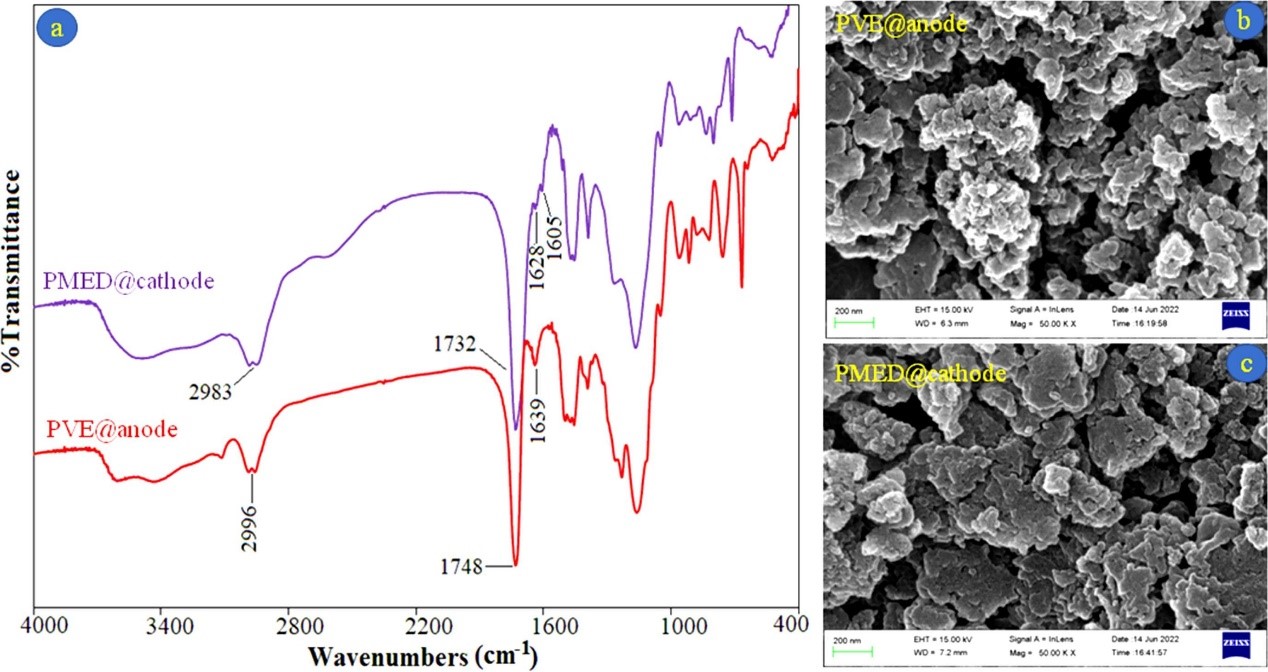
(a) FT-IR spectra of PVE@anode and PMED@cathode; (b) SEM image of PVE@anode; (c) SEM image of PMED@cathode.

