作 者:Lin, KD; Song, LH; Zhou, SY; Chen, D; Gan, J影响因子:3.512
刊物名称:CHEMOSPHERE
出版年份:2016
卷:155 页码: 266-273
Brominated phenolic compounds (BPCs) are a class of persistent and potentially toxic compounds ubiquitously present in the aquatic environment. However, the origin of BPCs is not clearly understood. In this study, we investigated the formation of BPCs from natural manganese oxides (MnOx)-catalyzed oxidation of phenol in the presence of Br-. Experiments at ambient temperature clearly demonstrated that BPCs were readily produced via the oxidation of phenol by MnOxin the presence of Br-. In the reaction of MnOxsand with 0.213μmol/L phenol and 0.34 mmol/L Br-for 10 min, more than 60% of phenol and 56% of Br-were consumed to form BPCs. The yield of BPCs increased with increasing concentrations of phenol and Br-. Overall, a total of 14 BPCs including simple bromophenols (4-bromophenol, 2,4-dibromophenol, and 2,4,6-tribromophenol), hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers (OH-PBDEs), and hydroxylated polybrominated biphenyls (OH-PBBs) were identified. The production of BPCs increased with increasing concentrations of Br-or phenol. It was deduced that Br-was first oxidized to form active bromine, leading to the subsequent bromination of phenol to form bromophenols. The further oxidation of bromophenols by MnOxresulted in the formation of OH-PBDEs and OH-PBBs. In view of the ubiquity of phenol, Br-, and MnOxin the environment, MnOx-mediated oxidation may play a role on the natural production of BPCs.
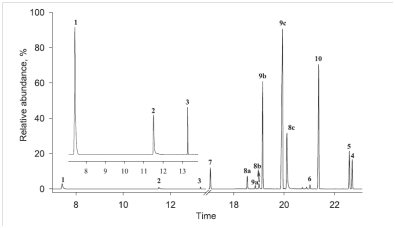
Fig. 3.A typical chromatogram (sum of the selective monitoring ions) for the gas chromatography-mass spectrometer analysis of the detected brominated products. The structuresand names of the identified compounds (1 to 10) are summarized in Table 1.

