作 者:Li, J;Liu, JC;Lu, HL; Jia, H; Yu, JY; Hong, HL;Yan,CL影响因子:3.512
刊物名称:CHEMOSPHERE
出版年份:2016
卷:144 页码: 2206-2213
Phenols exert a great influence on the dynamic process of Cd in the soil-plant interface. We investigated the influence of phenols on the biogeochemical behavior of cadmium in the rhizosphere ofAvicennia marina(Forsk) Vierh. All combinations of four levels of cadmium (0, 1, 2 and 4 mg/kg DW) and two levels of phenol (0 and 15 mg/kg DW) were included in the experimental design. We found that phenols facilitated increasing concentrations of exchangeable cadmium (Ex-Cd), acid volatile sulfide (AVS) and reactive solid-phase Fe (II) in sediments, and iron in plants, but inhibited Cd accumulation in iron plaque and roots. The concentrations of AVS and reactive solid-phase Fe (II) were significantly positively correlated with Cd treatment. As for the biogeochemical behavior of Cd in mangrove sediments, this research revealed that phenols facilitated activation and mobility of Cd. They disturbed the "source-sink" balance of Cd and turned it into a "source", whilst decreasing Cd absorption inA. marina. Additionally, phenols facilitated iron absorption in the plant and alleviated the Fe limit for mangrove plant growth.
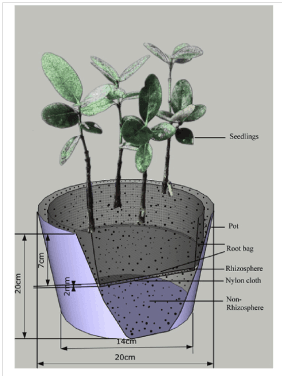
Fig. 1.Sketch of the rhizobox used in this study.

