作 者:Zhang, HJ; Peng, Y; Zhang, S; Cai, GJ; Li, Y; Yang, XJ;Yang, K; Chen, ZR; Zhang, J; Wang, H;Zheng, TL; Zheng, W影响因子:4.032
刊物名称:Frontiers in Microbiology
出版年份:2016
卷:7 页码: 602-602
Phaeocystis globosablooms can have negative effects on higher trophic levels in the marine ecosystem and consequently influence human activities. Strain KA22, identified as the bacteriumHahella, was isolated from coastal surface water and used to controP. globosagrowth. A methanol extract from the bacterial cells showed strong algicidal activity. After purification, the compound showed a similar structure to prodigiosin when identified with Q-Exactive Orbitrap MS and nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. The compound showed algicidal activity againstP. globosawith a 50% Lethal Dose (LD 50 ) of 2.24 µg/mL. The prodigiosin was stable under heat and acid environment, and it could be degraded under alkaline environment and natural light condition. The growth rates of strain KA22 was fast in 2216E medium and the content of prodigiosin in this medium was more than 70 µg/mL after 16 h incubation. The compound showed particularly strong algicidal activity againstProrocentrum donghaiense,P. Globosa, andHeterosigma akashiwo, but having little effect on three other phytoplankton species tested. The results of our research could increase our knowledge on harmful algal bloom control compound and lead to further study on the mechanisms of the lysis effect on harmful algae.
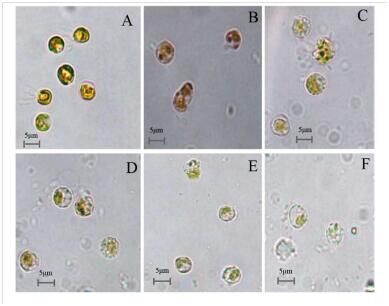
Fig.6.Microscopy images of the cellular morphology of prodigiosin-treatedP.globosecells. (A)Control cells;(B–F)12, 24, 36, 48, and 72h treatment. Scale bars=5μm.

