作 者:Cai, GJ; Yang, XJ; Lai, QL; Yu, XQ; Zhang, HJ; Li, Y;Chen, ZR; Lei, XQ; Zheng, W; Xu, H &Zheng, TL影响因子:5.295
刊物名称:Scientific Reports
出版年份:2016
DOI: 10.1038/srep20081 1
Algicidal microbes could effectively remove the harmful algae from the waters. In this study, we were concerned with the ecological influence of an algicide extracted fromStreptomyces alboflavusRPS, which could completely lyse thePhaeocystis globosacells within two days. In microcosms, 4μg/mL of the microbial algicide could efficiently removeP. globosacells without suppressing other aquatic organisms. Bioluminescent assays confirmed that the toxicity of microbial algicide at this concentration was negligible. Interestingly, the toxicity ofP. globosaexudates was also significantly reduced after being treated with the algicide. Further experiments revealed that the microbial algicide could instantly increase the permeability of the plasma membrane and disturb the photosynthetic system, followed by the deformation of organelles, vacuolization and increasing oxidative stress. The pre-incubation of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) verified that the rapid damages to the plasma membrane and photosynthetic system caused the algal death in the early phase, and the increasing oxidative stress killed the rest. The late accumulation and possible release of CAT also explained the decreasing toxicity of the algal culture. These results indicated that this microbial algicide has great potential in controlling the growth ofP. globosaon site.
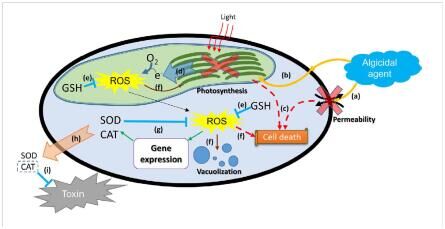
Fig. 8.The possible mechanism of how the microbial algicide produced byS. alboflavusRPS induced the lysis ofP. globosa.(a)~(i) indicate
different stages in the death process. Details were described in the article.

