作 者:Li, J; Yu, JY;Liu, JC;Yan, CL;Lu, HL; Kate, LS影响因子:2.961
刊物名称:MARINE POLLUTION BULLETIN
出版年份:2016
卷: 114 页码:733–741
P (phosphorus) and Fe (iron) are limiting elements and S (sulfur) is an important element of the biogeochemical cycle in the mangrove environment. To assess the effects of sulfur on the geochemical cycling of Fe and P at the sediment-plant interface, the speciation distributions of Fe, P and S in sediments were examined. The data showed that higher proportions of amorphous Fe, Fe-bound phosphate, chromium reducible sulfur and elemental sulfur were found in the rhizosphere, while more crystalline Fe, exchangeable phosphate and acid-volatile sulfide were determined in the non-rhizosphere. Sulfate application induced an increase in the Ex-P concentration, high P accumulation and high iron plaque deposition in the roots. In conclusion, sulfate applications had a significant influence on the geochemical cycling of Fe and P in the sediments. It significantly curtailed the Fe and P limit to plant growth and enhanced plant resistance to the rugged surroundings in mangrove.
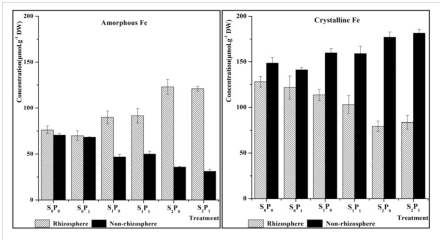
Fig. 3.Distributions of amorphous and crystalline Fe in the sediments of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere. Note: “amorphous Fe” and “crystalline Fe” indicate oxalate extracted and DCB extracted Fe respectively. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of the mean (n=3).

