作 者:Wang, Z; Zhou, XP; Lin, QX;Fang, WZ;Chen, XL
影响因子:2.806
刊物名称:PLOS ONE
出版年份:2017
卷: 12(5)The genes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) are important to vertebrate immune
system. In this study, two new MHC class I genes, designated as Egeu-UAA and Egeu-
UBA, were discovered in the vulnerable Chinese egret (Egretta eulophotes). Using a full
length DNA and cDNA produced by PCR and RACE methods, these two MHC class I loci
were characterized in the genome of the Chinese egret and were also found to be expressed
in liver and blood. Both new genes showed the expected eight exons and were similar to two
copies of the minimal essential MHC complex of chicken. In genetic diversity, 14 alleles (8
for UAA and 6 for UBA) in the MHC class I gene exon 3 were found in 60 individuals using
locus-specific primers and showed little polymorphism. Only three potential amino acid residues
were detected under positive selection in potential peptide-binding regions (PBRs) by
Bayesian analysis. These new results provide the fundamental basis for further studies to
elucidate the molecular mechanisms and significance of MHC molecular adaptation in vulnerable
Chinese egret and other ardeids, finding that have not been previously reported.
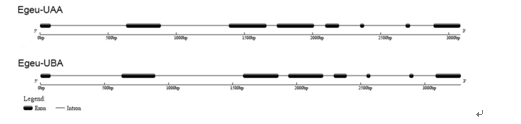
Fig 8.Schematic illustration of MHC class I genes in the Chinese egret.

