作 者:Fu, SJ;Cai, LZ; Cao, J; Chen, XW
影响因子:2.182
刊物名称: ESTUARIES AND COASTS
出版年份:2017
卷:40(5) 页码: 1437-1449
Investigations into nematode density and species assemblages have been conducted in different types of mangroves worldwide, but these studies have typically been limited to one type of plant or tree species. The invasive salt marsh grassSpartina alterniflorahas successively invaded native mangroves along the southern coasts of China during the preceding two decades. However, few meiofauna studies on the impacts ofS. alterniflorahave been conducted, and the consequences of this invasion on ecosystem composition and function remain unclear. The hypothesis of this study was that the spatial and seasonal distribution of nematode assemblages vary significantly among three native mangrove habitats (Kandelia obovata, Aegiceras corniculatum, andAvicennia marina) and between these habitats and a fourth habitat that was colonized byS. alterniflora, in Zhangjiang Estuary, China. Our results demonstrated that different species dominated in different habitats seasonally. Highly significant differences in density, number of species, diversity index, and maturity index were present among the four habitats. ANOSIM results revealed that there were significant differences in nematode assemblages among the four habitats and seasons, with theS. alterniflorahabitat exhibiting the lowest mean values of number of species, Shannon-Wiener diversity index, richness index, and maturity index in the four seasons. This suggests that the presence ofS. alternifloradisrupted nematode assemblages.
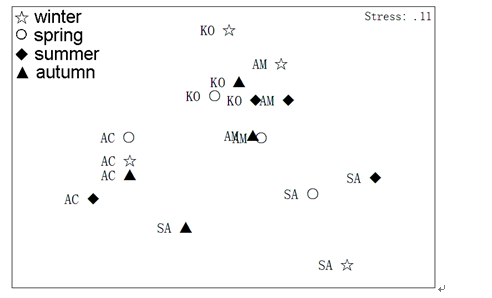
Fig. 9.Non-parametric multidimensional scaling analysis based on square-root-transformed nematode density from four habitats (KO,Kandelia obovata; AC,Aegiceras corniculatum; AM,Avicennia marina; SA,Spartina alterniflora) for different seasons

