作 者:Xu, XQ; Shi, L;Wang, MH影响因子:4.295
刊物名称:ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION
出版年份:2016
卷:218 页码: 1287-1297
In our earlier work,Tigriopus japonicuswere subjected to different mercuric chloride treatments (0 -50 μg/L in the seawater) for five generations (F0-F4), and they were subsequently resumed under clean environments for one generation, i.e., F5. Accumulative effects were hypothesized to participate in mercury (Hg) multigenerational toxicity, however phenotypic plasticity could be responsible for metal resistance in this copepod against the long term exposure. Here, we specifically investigated the proteome profiles in the F0, F2, and F5 copepods of the control and 50 μg/L metal treatment, respectively, so as to elucidate the action mechanisms for Hg toxicity/tolerance inT. japonicusunder the long term exposure. Functional enrichment analysis showed that a quite different proteomic response was observed in F5 compared with F0 and F2. Namely, the vast majority of enrichments were correlated with the down-regulated proteins in F0 and F2, whereas the enrichments for F5 were mostly attributable to the up-regulated proteins, suggesting that different mechanisms are responsible for Hg toxicity and tolerance (i.e., phenotypic plasticity). Hg toxicity prohibited many proteins in F0 and F2 which are related to several critical processes/pathways, e.g., protein translation, macromolecule metabolic process, DNA replication, cell cycle, cuticle organization, vitellogenesis, etc. In F5, many up-regulated proteins were enriched into compensatory systems, such as carbohydrate metabolism, myosin reorganizations, and stress-related defense pathway. Notably, glycolysis (an oxygen-independent pathway) was enhanced for energy allocation into metal detoxification and tolerance. Taken together, proteomics provides novel mechanistic insights into phenotypic plasticity used byT. japonicuswhen challenged with cumulative effects due to Hg multigenerational toxicity.
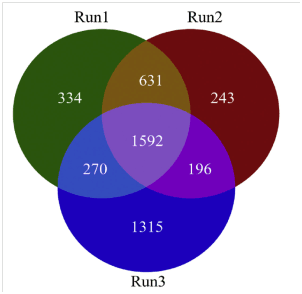
Fig. 1.Venn diagram showing the overlaps of identified proteins of the qualitative comparative proteomics of threeTigriopus japonicusproteome sets. One run set represents one generation under two concentration treatments, and two biological replicates were performed for each treatment. Note: run 1 was conducted for F0, run 2 for F2, and run 3 for F5.

