作 者:Huang, L.X., Zuo, Z.H., Zhang, Y.Y., andWang,C.G. 影响因子:3.507
刊物名称:AQUATIC TOXICOLOGY
出版年份:2015
卷:158 页码:157-164
There is a growing recognition that the toxic effects of chemical mixtures are been an important issue intoxicological sciences. Tributyltin (TBT) and benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) are widespread pollutants that occursimultaneously in the aquatic environments. This study was designed to examinecomprehensivelythecombined effects of TBT and BaP on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos using toxicogenomic approachcombined with biochemical detection and morphological analysis, and tried to gain insight into themechanisms underlying the combined effects of TBT and BaP. The results of toxicogenomic data indicated that: (1) TBT cotreatment rescued the embryos from decreased hatching ratio caused by BaP alone,while the alteration of gene expression (in this article the phrase gene expression is used as a synonymto gene transcription, although in is acknowledged that gene expression can also be regulated by, e.g.,translation and mRNA or protein stability) relative to zebrafish hatching in the BaP groups was resumedby the cotreatment with TBT; (2) BaP cotreatment decreased TBT-mediated dorsal curvature, and alleviated the perturbation of Notch pathway caused by TBT alone; (3) cotreatment with TBT decreasedBaP-mediated bradycardia, which might be due to that TBT cotreatment alleviated the perturbation inexpression of genes related to cardiac muscle cell development and calcium handling caused by BaPalone; 4) TBT cotreatment brought an antagonistic effect on the BaP-mediated oxidative stress and DNAdamage. These results suggested that toxicogenomic approach was available for analyzing combinedtoxicity with high sensitivity and accuracy, which might improve our understanding and predictabilityfor the combined effects of chemicals.
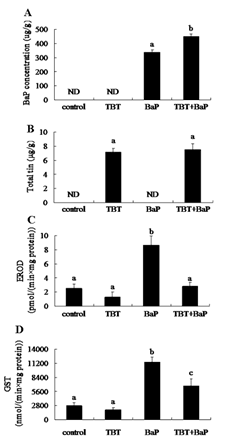
Fig.1.Concentrations of BaP (A), total tin (B), EROD (C) and GST (D) activity in zebrafish embryos after exposure for72 h. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3).Means of exposures not sharing a common letter are significantly different at p < 0.05 as assessed by one-way anova followed by the bonferroni’s test. nd="not" detected.

