作 者:Hong, H.Z., Shen, R., Liu, W.X., Li, D.M.,Huang, L.M.,Shi, D.L. 影响因子:2.961
刊物名称:MARINE POLLUTION BULLETIN
出版年份:2015
卷:101 页码:110-118
The composition of major hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) diastereoisomers, i.e.α-,β-, andγ-HBCDs, in marine biota is different from that of the commercially available form (technical HBCD), which is used extensively for toxicological studies. To properly evaluate the impact of HBCDs, the embryos ofOryzias melastigmawere used to examine the developmental toxicity of the individual diastereoisomers. Results showed that HBCD diastereoisomers at the environmentally realistic concentrations in the embryos induced malformation rate and heartbeat, and caused the appearance of apoptotic heart. In addition,α-,β-, andγ-HBCDs had similar potency to stimulate the generation of reactive oxygen species, consequently leading to apoptosis inO.melastigmaembryos. The order of the developmental toxicity ofα-,β-, andγ-HBCDs inO.melastigmaembryos was different fromthat in zebrafish embryos studied previously, which highlighted the importance of using species from both fresh and salt water for toxicity assessment.
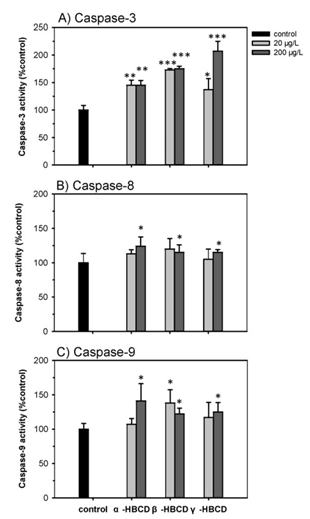
Fig. 5.Induction of the activities of caspase-3 (A), caspase-8 (B) and caspase-9 (C) inO. melastigmaembryos after exposure to 0, 20, and 200 μg/L of α-, β-, and γ-HBCDs. The values are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 4). Data presentation is same as Fig. 2.

