作 者:Xie, Y.Y.,Huang, B.Q., Lin, L.Z., Laws, E.A.,Wang, L., Shang, S.L., Zhang, T.L., and Dai, M.H. 影响因子:3.395
刊物名称:JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: Oceans
出版年份:2015
卷:120 页码:4187-4204
Many recent models for retrieval of primary production in the sea from ocean-color data aretemperature based. But previous studies in low latitudes
have shown that models that include phytoplanktoncommunity structure can have improved predictive capability. In this study, we measured photosyntheticparameters from photosynthesis-irradiance (P-E) experiments, phytoplankton absorption coefficients,and phytoplankton community structure derived from algal pigments during four cruises in the northernSouth China Sea (NSCS). The maximum quantum yield of CO2(φCm) and the chlorophylla-normalized P-Ecurve light-limited slope (αB) varied significantly with the blue-to-red ratio of phytoplankton absorptionpeaks (aph(435)/aph(676)) (p<0 .001,r="-0.459" and-0.332, respectively). the unexplained variability couldbe due in part to the absorption associated with nonphotosynthetic pigments. the chlorophylla-normalizedlight-saturated photosynthetic rate (PBm) at the surface showed a unimodal distribution over the chlorophyllarange during the spring and summer, and significantly increased whenProchlorococcuswasoutcompeted by other picophytoplankton (p<0 .01). almost 60% of the variance ofPBmcould be explainedby a piecewise regression with phytoplankton absorption coefficients and pigment markers. Unlike previousstudies, our data showed that changes ofPBmwere unrelated to the size structure of phytoplankton.Although a temperature-based approach could not effectively predictαBandPBmin the NSCS, a trophicbasedapproach can be used for assignment of these parameters in a regional primary production modelusing ocean-color data.
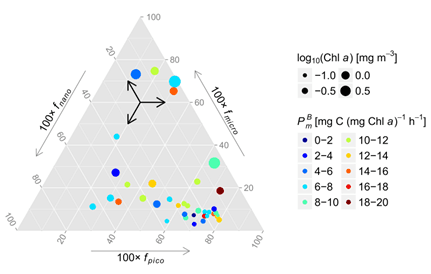
Fig.8.The ternary plot of chlorophyll a-normalized light-saturated photosynthetic rate PBmon surface (at optical depths ζ< 1) as function of proportions of phytoplankton size classes (fmicro, fnano,andfpico) and chlorophyll a.

