作 者:Lei, W.,Fang, W.Z., Lin, Q.X., Zhou, X.P.,Chen, X.L.
影响因子:2.339
刊物名称:Immunogenetics
出版年份:2015
卷:67页码 : 463–472
Genes of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) are valuable makers of adaptive genetic variation in evolutionary ecology research, yet the non-classical MHC genes remain largely unstudied in wild vertebrates. In this study, we have characterized the non-classical MHC class II gene,Egeu-DAB4, in the vulnerable Chinese egret (Ciconiiformes, Ardeidae,Egrettaeulophotes). Gene expression analyses showed thatEgeu-DAB4gene had a restricted tissue expression pattern, being expressed in seven examined tissues including the liver, heart, kidney, esophagus, stomach,gallbladder, and intestine, but not in muscle. With respect to polymorphism, only one allele of exon 2 was obtained fromEgeu-DAB4using asymmetric PCR, indicating thatEgeu-DAB4is genetically monomorphic in exon 2. Comparative analyses showed thatEgeu-DAB4had an unusual sequence,with amino acid differences suggesting that its function may differ from those of classical MHC genes.Egeu-DAB4genewas only found in 30.56–36.56 % of examined Chinese egret individuals. Phylogenetic analysis showed a closer relationship betweenEgeu-DAB4and the DAB2 genes in nine other ardeid species. These new findings provide a foundation for further studies to clarify the immunogenetics of non-classical MHC class II gene in the vulnerable Chinese egret and other ciconiiform birds.
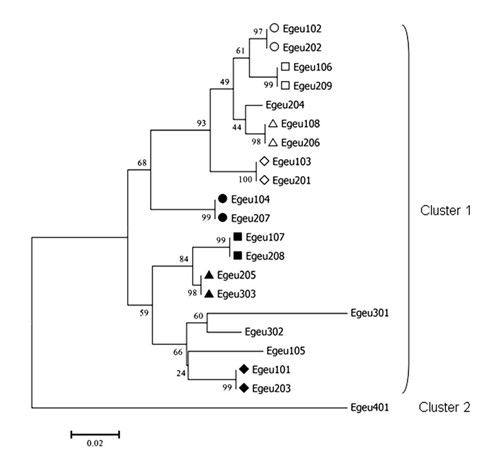
Fig.4.Maximum likelihood tree of the 21 confirmedEgeu-DABexon 2 nucleotide sequences. Theeight pairs of identically shared alleles amongEgeu-DAB1 – 3genes are respectively indicated by the same geometric patterns(e.g., hollow circle) to the left of the allele name

