作 者:Wu, G.R., Hong, H.L., andYan, C.L.影响因子:2.030
刊物名称:International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
出版年份:2015
卷:12 期:4 页码:7244-7253
Mangrove wetlands serve as both a sink and source for arsenic (As), as mangrove plants are able to uptake and accumulate As. The present study used pot experiments to evaluate As accumulation and translocation in mangrove (AegicerascorniculatumL.) seedlings grown in As contaminated soils. Results indicated thatA.corniculatumseedlings grew normally under As stress with minute growth inhibition and biomass reduction at different As treatment concentrations in a range of 0–150 mg·kg−1. As concentrations in roots, stems and leaves were increased with increasing As treatment concentrations, but As accumulated mainly in roots, with accumulation rates of 74.54%–89.26% of the total As accumulation. In particular, relatively high bioconcentration factor (BCF) in root (2.12–1.79), low BCF in stem (0.44–0.14) and leaf (0.06–0.01), and thereby a low translocation factor (TF) in stem/root (0.21–0.08) and leaf/root (0.02–0.008)were observed. These results demonstrated thatA. corniculatumis an As excluder with the innate capacity to tolerate As stress and root tissues may be employed as a bio-indicator of As in polluted sediments. Additionally,A. corniculatumis a potential candidate mangrove species for As phytostabilization in tropical and subtropical estuarine wetlands.
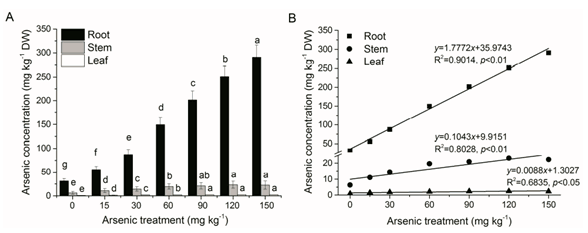
Fig.1.Effects of As treatments on (A) As concentrations in root, stem and leaf, and (B) linear relationship between As treatment concentrations and As concentrations in root, stem and leaf inA. corniculatumseedlings. Values are mean ± SE (n = 5). Different letters above comparable columns in Figure 1A indicate significant differences at p < 0.05.

