Juan Chen, Wen-Hua Wang, Ting-Wu Liu, Fei-Hua Wu, Hai-Lei Zheng*.Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2013.64: 41–51.
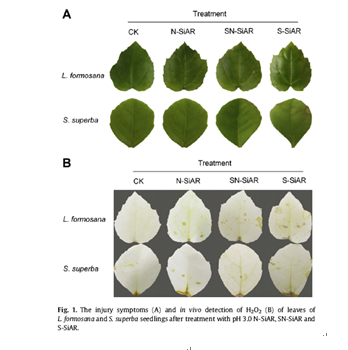
To study whether differential responses occur in photosynthesis and antioxidant system for seedlings ofLiquidambar formosana, an acid rain (AR)-sensitive tree species and Schima superba, an AR-tolerant treespecies treated with three types of pH 3.0 simulated AR (SiAR) including sulfuric-rich (S-SiAR), nitric-rich(N-SiAR), sulfate and nitrate mixed (SN-SiAR), we investigated the changes of leaf necrosis, chlorophyllcontent, soluble protein and proline content, photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics,reactive oxygen species production, membrane lipid peroxidation, small molecular antioxidant content,antioxidant enzyme activities and related protein expressions. Our results showed that SiAR significantlycaused leaf necrosis, inhibited photosynthesis, induced superoxide radical and hydrogen peroxide generation,aggravated membrane lipid peroxidation, changed antioxidant enzyme activities, modifiedrelated protein expressions such as Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD), L-ascorbate peroxidase (APX, EC1. 11. 1. 11), glutathione S transferase (GST, EC 2. 5. 1. 18) and Rubisco large subunit (RuBISCO LSU), alterednon-protein thiols (NPT) and glutathione (GSH) content in leaves of L. formosana and S. superba. Takentogether, we concluded that the damages caused by SiAR in L. formosana were more severe and sufferedfrom more negative impacts than in S. superba. S-SiAR induced more serious damages for the plants thandid SN-SiAR and N-SiAR.