LIN Jing , ZHENG Wei,
TIAN Yun, WANG Guizhong, ZHENG Tianling.J. Ocean Univ. China, 2013. 12 (3):
385-391
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) have led to
extensive ecological and environmental issues and huge economic losses. Various
HAB control techniques have been developed, and biological methods have been
paid more attention. Algicidal bacteria is a general designation for bacteria
which inhibit algal growth in a direct or indirect manner, and kill or damage
the algal cells. A metabolite which is strongly toxic to the dinoflagellateAlexandrium tamarensewas produced by
strain DH46 of the algalysing bacterium Alteromonas sp. The culture conditions
were optimized using a single-factor test method. Factors including carbon
source, nitrogen source, temperature, initial pH value, rotational speed and
salinity
were studied. The results showed that the cultivation of the bacteria
at 28℃and 180 r min-1with
initial pH 7 and 30 salt contcentration favored both the cell growth and the
lysing effect of strain DH46. The optimal medium composition for strain DH46
was determined by means of uniform design experimentation, and the most
important components influencing the cell density were tryptone, yeast extract,
soluble starch, NaNO3and MgSO4. When the following
culture medium was used (tryptone 14.0g, yeast extract 1.63g, soluble starch
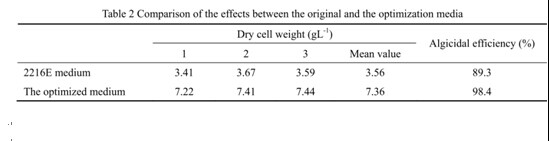
5.0g, NaNO31.6g, MgSO42.3g in 1L) , the largest bacterial dry weight (7.36gL-1)
was obtained, which was an enhancement of 107% compared to the initial medium;
and the algal lysis rate was as high as 98.4% which increased nearly 10% after
optimization.
返回

