Xiao-xin CHEN, Xiao-bing WU, Wei-ming CHA,
Hui-ling FENG,Yan SHI, Han-tao ZHOU, Qing-xi CHEN.Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE
B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology),2013. 14(10):903-915.
In this research, the conditions for extraction of phenolics from
leaves of Ficus virens were optimized usingresponse surface methodology (RSM).
The extraction abilities of phenolics (EAP) and flavonoids (EAF),
the2,2-diphenyl-1-pierylhydrazyl (DPPH) free-radical scavenging potential, and
the ferric reducing/antioxidant power(FRAP) were used as quality indicators.
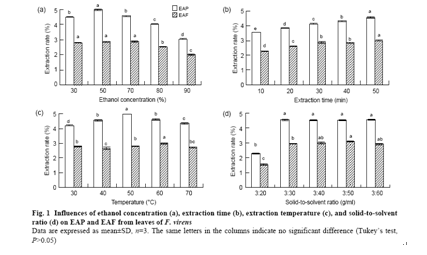
The results of single-factor experiments showed that temperature, ethanolconcentration,
extraction time, and the number of extraction cycles were the main influencing
variables, and theseprovided key information for the central composite design.
The results of RSM fitted well to a second degree polynomialmodel and more than
98% of the variability was explained. The ideal extraction conditions for EAP,
EAF, DPPHfree-radical scavenging potential, and FRAP were obtained. Considering
the four quality indicators overall, the idealextraction conditions were 58%
ethanol at 57 °C for 37 min with three extraction cycles. At the ideal
extraction conditions,the values of EAP, EAF, DPPH free-radical scavenging
potential, and FRAP were 5.72%, 3.09%, 58.88 mgascorbic acid equivalent (AAE)/g
dry weight (DW), and 15.86 mg AAE/g DW, respectively. In addition, linear
correlationswere observed between EAP, EAF, and antioxidant potential.
返回

