Lu HL, Y Zhang, BB Liu, JC Liu, J Ye and CL Yan.Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011. 196: 263-269.
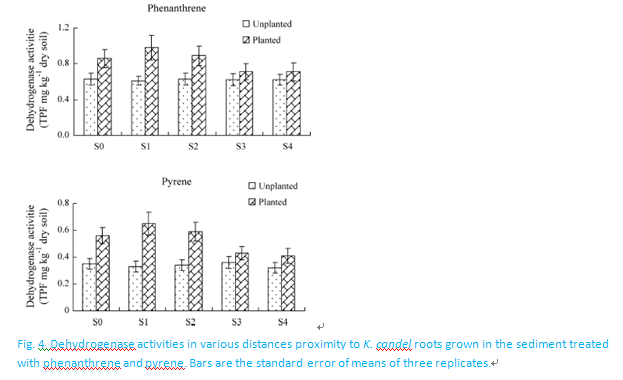
A greenhouse experiment was conducted to evaluate degradation gradient of spiked phenanthrene (Ph, 10 mg kg−1) and pyrene (Py, 10 mg kg−1) in rhizosphere of mangroveKandelia candel(L.) Druce. Rhizosphere model system was set up using a self-design laminar rhizoboxes which divided into eight separate compartments at various distances from the root surface. After 60 days of plant growth, presence of the plant significantly enhanced the dissipation of Ph (47.7%) and Py (37.6%) from contaminated sediment. Higher degradation rates of the PAHs were observed at 3 mm from the root zone (56.8% Ph and 47.7% Py). The degradation gradient followed the order: near rhizosphere > root compartment > far-rhizosphere soil zones for both contaminants where mangrove was grown. Contribution of direct plant uptake and accumulation of Ph and Py were very low compared to the plant enhanced dissipation. By contrast, plant-promoted biodegradation was the predominant contribution to the remediation enhancement. The correlation analysis indicates a negative relation between biological activities (microbial biomass carbon, dehydrogenase, urease, and phosphatase activity) and residual concentrations of Ph and Py in planted soils. Our results suggested that mangrove rhizosphere was effective in promoting the depletion of aromatic hydrocarbons in contaminated sediments.