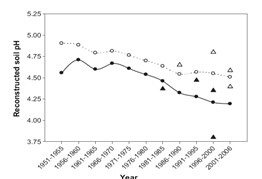
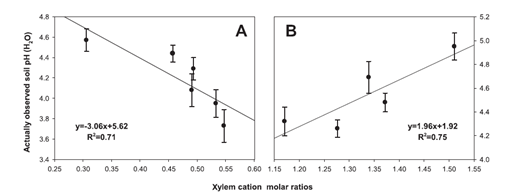
Chen L., Wu F.H., Liu T.W., Chen J., Li Z.J.,Pei Z.M., Zheng H.L.*Environmental Pollution, 2010.158: 3219-3224To assess the suitability of dendrochemistry as an indicator of soil acidification, soil chemistry and tree ring information ofAbies fabriwere measured at two distinct sites (severe acid deposition site-Emei Mountain and clean site-Gongga Mountain) of the subalpine forest ecosystems of western Sichuan, southwest China. The actual soil acidity (pH) was significantly correlated with some of the recent xylem cation (Ca, Mg, Mn, Al, Sr and Ba) concentrations and their molar ratios. Xylem Ca/Mg and Ca/Mn ofAbies fabriwere ultimately selected to reconstruct the historical changes of soil pH in Emei Mountain and Gongga Mountain, respectively. The validity of those rebuild was also verified to a certain extent. We conclude that xylem cation molar ratios ofAbies fabriwere superior to the single cation concentration in soil acidity rebuild at the study sites due to normalizing for concentration fluctuations.