Lin Q.; Chen L.; Zhang J.; Wang L.; Yu X. and Guo Q. 2023. Plant and Soil 488(1-2): 451-63.
Background and aims
Fine roots (diameter<2 mm) are the component of belowground biomass, which are help to maintain sediment volume and resist soil compaction in mangroves. In addition, fine root turnover contributes to belowground carbon stocks. This study focused on root zone dynamics and aimed to quantify the composition of live and dead fine roots and analyze their functions during root zone expansion and belowground carbon accumulation.
Methods
Shallow surface elevation tables for measuring root zone expansion were set up in Dongzhaigang Bay of Hainan Province, China; root cores and ingrowth bags for measuring fine root biomass and turnover rates were used in four typical mangrove forests.
Results
Fine root biomass contributed over 60% to belowground roots, and was mainly composed of up to 69.25% dead fine roots. Fine root turnover rates ranged from 0.10 to 0.22 per year within the four forests, showing the fastest in Bruguiera forest, followed by Kandelia forest, Sonneratia plantation, and Rhizophora forest. Root zone expansion rates ranged from 0.55 to 1.28 mm yr−1, and were positively related to live fine root biomass within the upper 50 cm layer of sediment in the four forest types (R2=0.625, P=0.0022).
Conclusions
Live fine root biomass took up less than 30.75% of belowground biomass, but remarkably supported 62.50% of root zone expansion in mangroves. Turnover rates of fine roots significantly contributed to the highly dynamic changes in the carbon processes of sub-surface sediment.
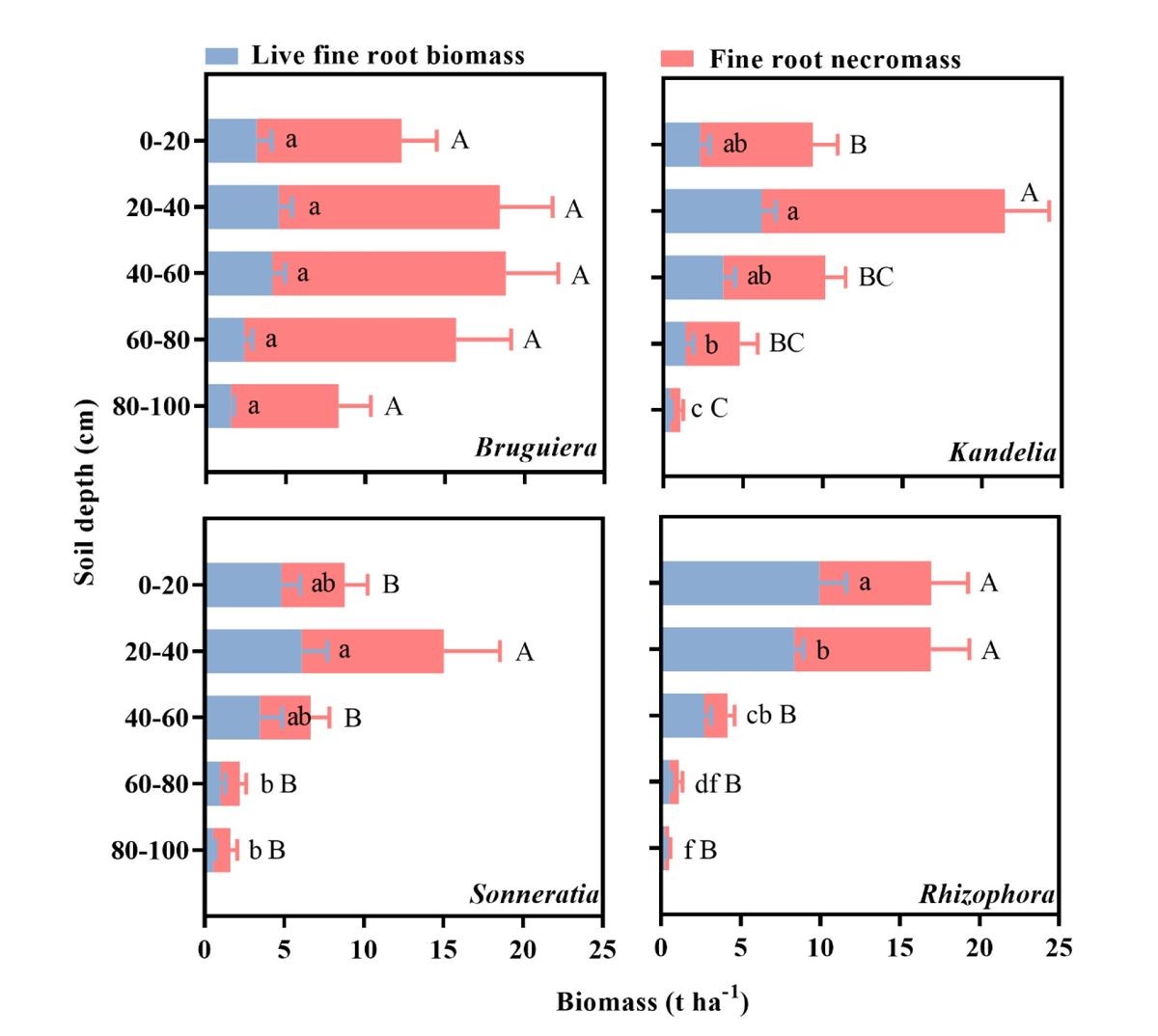
Biomass of live fine roots and dead fine roots (mean±se) of the mangrove forests in Dongzhaigang Bay. Different letters denote significant differences (P< 0.05) among the four forests

