作 者:Li, H.J., Xia, Y., Rao, Y.Y., Liu, S.X., Zhang,J.J.,Cai, L.Z. 影响因子:1.214
刊物名称:Aquatic biology
出版年份:2015
卷:24 页码: 17-24
The Chinese horseshoe crabTachypleus tridentatusis an endangered marine benthic species of great biomedical value and scientific significance. In this study,T. tridentatushemocyte transcriptome was sequenced to rapidly develop molecular resources using the Illumina paired-end sequencing platform. Deep sequencing generated a total of 38 402 764 reads that consisted of 7.7 Gbp raw data, which were assembled into 38 759 unigenes with an average length of 668.6bp. A total of 608 microsatellite loci and 71 959 high-confidence single nucleotide polymorphisms were discovered. All the assembled unigenes were annotated by running BLASTx similarity searches on Nr, Swiss-Prot, COG, and KEGG databases; of which17 446 (45.0%) unigenes showed significant matches(E-value <1e −5) to known sequences in public databases. As determined through gene ontology annotation and KEGG pathway mapping, the functional annotation of the unigenes signified diverse biological functions and processes. Transcripts potentially involved in immune defense were identified among these genes. These transcripts included pattern recognition receptors, stress response genes, complement components, and immune effectors. This study provides important insights into the transcript sequences ofT. tridentatus, which may facilitate studies on the conservation genetics and development of biomedical applications forT. tridentatus.
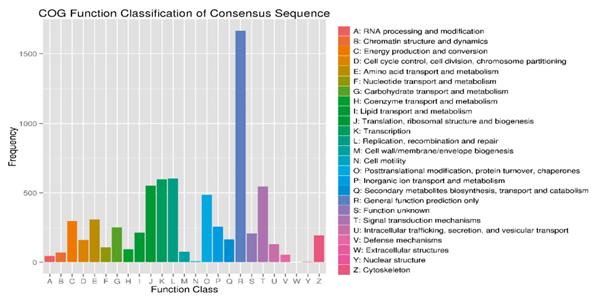
Fig.6.Classification according to clusters of orthologous groups (COG)

